Why in News?
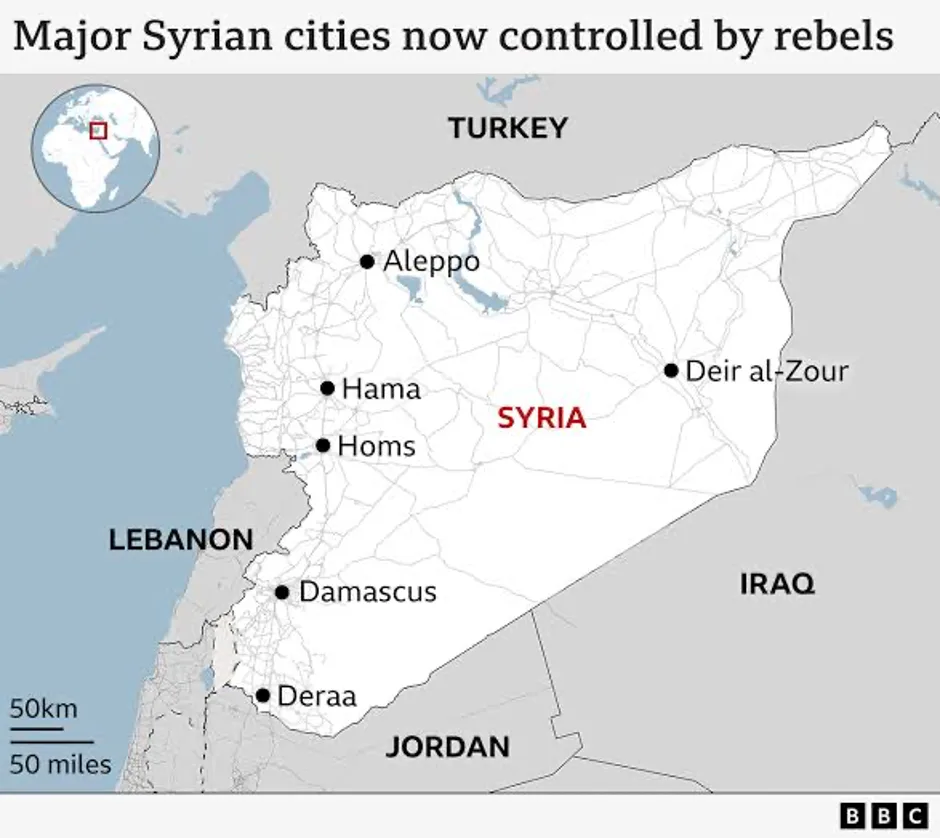
Syria’s civil war has entered a new phase with a sudden attack by the military opposition command on forces loyal to President Bashar al-Assad. They have taken control of major cities, including Aleppo, Hama, Homs, and Daraa. The political situation in Syria has become more uncertain.
Introduction of Syrian Civil War:
- The Syrian Civil War is one of the most devastating and complex conflicts of the 21st century.
- It began in 2011 and has resulted in massive loss of life, widespread displacement, and severe damage to the country’s infrastructure.
- The conflict started as a series of protests demanding political reforms, but it quickly escalated into a brutal war involving multiple factions, both local and international.
- The war is significant not only for humans but also for its regional instability and global impact.
Source: https://bbc.com/news/articles/c2ex7ek9pyeo
Historical Background:
- The Assad Regime:
- Hafez al-Assad took power in 1970, establishing an authoritarian regime based on Ba’athist ideology.
- After Hafez’s death in 2000, his son, Bashar al-Assad, succeeded him. Although Bashar was initially seen as a potential reformer, he quickly consolidated power and maintained strict control over the country.
- Political Landscape of Syria Before the War:
- Syria was historically a secular state, with its government dominated by the Alawite minority (an offshoot of Shia Islam), while the majority of the population is Sunni Muslim.
- The Assad regime maintained a delicate balance of power by relying on military repression, loyalist networks, and sectarian divisions.
- The Arab Spring Impact on Syria:
- In 2011, the Arab Spring, a wave of protests and revolutions across the Middle East, inspired Syrians to demand greater freedoms and an end to corruption and repression.
- Initially, peaceful protests erupted in Syria, but the government’s violent response to demonstrations quickly turned the situation into an armed rebellion, marking the beginning of the Syrian Civil War.
|
Key Points About Syria:
Source: https://bbc.com/news/articles/c2ex7ek9pyeo |
Causes of the Conflict:
- Economic Challenges and Inequality
- Syria faced significant economic hardship before the war, with high unemployment, poverty, and corruption widespread.
- The rural population struggled due to droughts, poor agricultural policies, and economic inequality.
- Sectarian Tensions in Syrian Society
- Syria’s diverse population is made up of Sunni Muslims, Alawites, Christians, Kurds, and other minorities.
- Under the Assad regime, the Alawite minority had disproportionate political and military power.
- Authoritarian Governance and Repression
- Bashar al-Assad’s government maintained tight control through military repression, surveillance, and political suppression.
- The regime was known for its lack of political freedoms, crackdown on dissent, and censorship, creating an atmosphere of fear and frustration.
- Catalyst: The 2011 Protests:
- Inspired by the Arab Spring, peaceful protests began in March 2011 in Daraa, calling for political reform, the release and an end to government corruption. The Assad regime turned these peaceful demonstrations into an armed rebellion.
Timeline of Key Events:
- Initial Protests (2011): The Spark of Rebellion In March 2011, protests broke out in Daraa, a city in southern Syria.
- Escalation to Civil War (2012) By 2012, the situation escalated into an all-out civil war. The initially peaceful protests evolved into armed conflict. Rebel groups began to take control of various areas, including parts of major cities like Aleppo and Homs.
- Rise of Rebel Groups and External Intervention (2013–2014) Between 2013 and 2014, numerous rebel factions emerged, including the Free Syrian Army (FSA), but divisions and infighting weakened their efforts. Islamist groups like Al-Nusra Front and ISIS also gained ground, further complicating the conflict. International actors, including Turkey, the United States, and Gulf states, began to intervene by supporting various rebel groups, while Russia and Iran deepened their support for the Assad government.
- Emergence of the Islamic State (ISIS) In 2014, the conflict took a darker turn with the rise of ISIS. This group declared a caliphate and was known for its unique tactics. ISIS’s rapid expansion drew international attention.
- Turning Points Over the next several years, there were key turning points in the war. However, despite these victories, the war’s devastation continued, with no clear resolution in sight.
Major Players in the Conflict:
- The Syrian Government and Its Allies: Under Bashar al-Assad, the regime received extensive support from Russia, which provided military aid, and Iran, which sent both military advisors and fighters. Hezbollah, a Lebanese militant group, also played a critical role.
- Opposition and Rebel Groups: The Free Syrian Army (FSA), initially formed by defectors from the Syrian military, was one of the first major rebel factions. Over time, various other groups, including Kurdish forces such as the YPG/YPJ, also became key players.
- International Players: The United States and Western Allies supported various opposition groups, while Turkey pursued its own interests, primarily opposing Kurdish autonomy. The United Nations also played a limited role.
Impact of the Syrian Civil War:
- Humanitarian Crisis
- Over 300,000 people have lost their lives due to the conflict, and millions of others have been displaced.
- The war has created one of the largest refugee crises in history, with millions fleeing to neighboring countries and beyond.
- 80% of children in Syria have been deeply affected, facing trauma, loss, and a lack of access to education and healthcare. The country’s basic infrastructure has been destroyed, with roads, schools, electricity, and water systems heavily damaged or completely ruined.
- Economic and Social Impact
- The war has also caused a massive economic crisis. The country’s GDP has shrunk by over 50% since the conflict began, leading to widespread poverty and unemployment.
- The Syrian pound has plummeted in value, resulting in currency devaluation and rising inflation.
- The economic destruction has led to severe hardship for the people, with essential goods becoming unaffordable for many.
International Response:
- Diplomatic Efforts and Peace Talks: Multiple rounds of peace negotiations have taken place, including the Geneva talks and Astana process, but no lasting solution has been reached.
- Role of the United Nations: The UN has provided humanitarian aid and facilitated peace talks, but has faced challenges due to political divisions among member states.
- Intervention of Countries: Countries like the U.S., Russia, and Turkey have intervened, often pursuing their own interests.
- Effectiveness of Sanctions: Sanctions imposed on the Syrian government have aimed to pressure Bashar al-Assad, but they had limited political impact.
The Syrian Civil War has caused immense destruction, loss of life, and displacement. It has devastated Syria’s economy and infrastructure, leaving the country in ruins. The future of Syria remains uncertain, with ongoing challenges in rebuilding and achieving peace.
Explore our Books: https://apnipathshala.com/product-category/books/
Explore Our test Series: https://tests.apnipathshala.com/