Why in News?
India-Sri Lanka Strengthen Bilateral Ties: Sri Lankan President Anura Kumara Dissanayake was on a three-day official visit to India. This was his first foreign trip since assuming office. During his visit, he held extensive discussions with Prime Minister Narendra Modi on strengthening bilateral ties, focusing on areas such as defence, trade, and investment.
Key Highlights of the India-Sri Lanka Visit:
- Bilateral Ties Strengthened: The leaders reaffirmed their commitment to advancing the India-Sri Lanka partnership for mutual benefit, emphasizing historical, cultural, and geographic ties.
- Support During Economic Crisis: Sri Lanka appreciated India’s unwavering support during its 2022 economic crisis and ongoing assistance for economic recovery and growth.
- Debt Restructuring Commitments: India played a significant role in Sri Lanka’s debt restructuring process, co-chairing the Official Creditor Committee and providing financial assistance to ease repayment burdens.
- Capacity Building and Training: India will train 1,500 Sri Lankan civil servants over five years and expand training programs across various sectors, including defence and governance.
- Connectivity Initiatives: Both sides agreed to restore the Rameswaram-Talaimannar passenger ferry service and explore opportunities for Kankesanthurai port development with India’s support.
- Digital Transformation: Both countries plan to implement Sri Lanka Unique Digital Identity (SLUDI) and expand digital financial systems like UPI to enhance transparency and efficiency in governance.
- Energy Collaboration: Both countries agreed for the Sampur solar project, exploring offshore wind energy, and advancing an India-Sri Lanka power grid interconnection.
- defence and Maritime Security: They agreed for cooperation in maritime surveillance, joint exercises, and capacity building, emphasising shared security interests in the Indian Ocean Region.
- Cultural and Tourism Promotion: They agreed to boost air connectivity, including new flight routes between India and Sri Lanka, and promoting religious and cultural tourism.
- Economic Partnerships: They agreed to strengthen trade and investment ties through INR-LKR trade mechanisms, a bilateral economic and technical cooperation agreement, and investment in Sri Lanka’s key sectors.
- Fisheries Issues: Leaders emphasized resolving fisheries disputes through dialogue and humanitarian approaches, avoiding conflict and supporting sustainable fishing practices.
- Regional and Global Cooperation: India reaffirmed support for Sri Lanka’s BRICS membership bid and its leadership role in IORA and BIMSTEC frameworks.
- Innovation and Education: Both countries plan to enhance R&D collaboration in agriculture, health, and digital technologies while fostering partnerships between academic and technology institutions.
- Strategic Shift in Partnerships: The transition from debt-driven models to investment-focused collaborations was emphasised as a sustainable approach to Sri Lanka’s development.
India-Sri Lanka Relations:
Historical Background of India-Sri Lanka Relations:
- India and Sri Lanka share over 2,500 years of cultural, religious, and linguistic ties rooted in shared history.
- Sri Lanka’s first mention is in the Ramayana, where Lord Rama defeated Ravana, who had held Sita captive in Lanka.
- The introduction of Buddhism to Sri Lanka by Emperor Ashoka’s son Mahinda in the 3rd century BCE is a significant historical milestone.
- Anuradhapura, the ancient capital of Sri Lanka, came under Chola control in 993 CE, symbolizing Indian influence on Sri Lanka’s early political history.
- India-Sri Lanka Relations Before Independence: Trade, migration, and cultural exchanges flourished between the two regions since ancient times.
- The Chola, Chera, and Chalukya dynasties played prominent roles in shaping Sri Lanka’s historical interactions with India.
- Sri Lanka, although a British colony, was administered separately from British India during the colonial period.
- Post-Independence India-Sri Lanka Relations: Bilateral ties were formalized after independence, fostering mutual cooperation in multiple areas.
-
During the 30-year conflict between the Sri Lankan government and the LTTE (Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam), India supported the sovereign rights of Sri Lanka to act against terrorism.
-
Developmental assistance and infrastructure projects in Northern and Eastern Sri Lanka have strengthened ties.
-
Political Relations between India and Sri Lanka:
The political relations between India and Sri Lanka have always been characterised by frequent high-level exchanges, which have continuously fostered mutual cooperation and understanding.
- 2015: Visit by Sri Lankan President Maithripala Sirisena to India: The relationship between India and Sri Lanka took a significant step forward in February 2015 when Sri Lanka’s newly elected president, Maithripala Sirisena, made his first visit to India. The visit set the stage for improved diplomatic relations between the two countries.
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s Visit in March 2015: In March 2015, Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi visited Sri Lanka. He became the first Indian prime minister to visit Sri Lanka in 28 years. During his visit, he focused on strengthening ties, enhancing economic cooperation, and addressing security concerns.
- June 2019: Easter Sunday Attacks: The political relationship further strengthened in June 2019 when Prime Minister Narendra Modi visited Sri Lanka following the horrific Easter Sunday attacks. His visit was aimed at expressing India’s solidarity with the Sri Lankan people during their time of crisis.
- Bilateral Vision: One of the key developments in this area came in 2023 when former President Wickremesinghe signed a “Vision Document” that focused on enhancing connectivity and promoting economic partnerships. This initiative covered areas such as renewable energy, solar energy projects, and better digital payment systems between the countries.
Commercial Relations between India and Sri Lanka:
- ISFTA Implementation (2000): Since the implementation of the ISFTA (India-Sri Lanka Free Trade Agreement) in 2000, Sri Lankan exports to India have seen significant growth, with over 60% of Sri Lanka’s total exports to India benefiting from ISFTA in recent years.
- Sri Lankan Investment in India: Leveraging India’s dynamic economy and large market, Sri Lankan businesses have increasingly invested in India.
- Open Sky Agreement: To improve connectivity between the two nations, India and Sri Lanka signed an Open Sky Agreement, enhancing air transport links.
- Largest Trade Partner: India has traditionally been one of Sri Lanka’s largest trading partners and remains the largest trading partner within SAARC. According to the Department of Commerce (DoC), bilateral trade reached USD 5.5 billion in FY 2023-24, with India’s exports at USD 4.1 billion and Sri Lanka’s exports at USD 1.4 billion.
- ETCA Proposal: To further expand the scope of the Free Trade Agreement (FTA) and strengthen rules of origin, an Economic and Technology Cooperation Agreement (ETCA) was proposed, covering both goods and services.
- FDI Contributions: India is not only Sri Lanka’s largest trading partner but also the largest contributor to Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) in Sri Lanka, with cumulative FDI reaching about USD 2.2 billion by 2023.
Cultural and Educational Relations between India and Sri Lanka
- Cultural Cooperation Agreement (1977): The Cultural Cooperation Agreement signed by the governments of India and Sri Lanka on November 29, 1977, in New Delhi serves as the foundation for periodic cultural exchange programs between the two countries.
- Swami Vivekananda Cultural Centre (SVCC): Since its establishment in 1998, the Swami Vivekananda Cultural Centre (SVCC) at the Indian High Commission in Colombo has played a significant role in deepening cultural ties and promoting people-to-people relations between India and Sri Lanka.
- Key Cultural Cooperation Initiatives:
- India Fund at the Colombo Public Library and establishment of India Corners in various universities.
- Sacred Kapilavastu Relics Exhibition in Sri Lanka in 2012 to mark the 2600th year of Buddha’s enlightenment (Sambodhitva Jayanti).
- First Flight from Colombo to Kushinagar (2021): In October 2021, on Shubha Vappoya Day, the first flight from Colombo to Kushinagar was launched.
- Gifts of Buddha Statue: Recently, a Buddha statue was gifted to the Dharmayathanya Temple in Sri Lanka.
- ICCR Chairs in Sri Lankan Universities: Long-term ICCR Chairs for Hindi were established at Kelaniya University and Sabaragamuwa University.
Development Cooperation Between India and Sri Lanka:
- Humanitarian Assistance: India played a first responder role during the COVID-19 pandemic, supplying vaccines and essential medicines, including a donation of 500,000 doses of Covishield vaccines and 100,000 Rapid Antigen Test (RAT) kits.
- Economic Assistance during Crisis: During the economic crisis in 2022, India provided nearly 4 billion USD in multifaceted support to Sri Lanka.
- Major Development Projects: India’s development cooperation with Sri Lanka is one of the most significant pillars of their bilateral relationship, involving 5 billion USD in concessional loans/loan swap agreements and 600 million USD in grants.
- Housing Project: The largest grant-funded project is the Indian Housing Project, which involves the construction of 60,000 houses under four phases, costing over 1,800 crore INR. Phase IV includes 10,000 houses for workers in the Bagan area, in line with the announcement made by Prime Minister Narendra Modi in May 2017.
- Digital Identity Project: India is also providing a 300 crore INR grant to implement the Sri Lanka Unique Digital Identity Project.
Defence and Security Cooperation Between India and Sri Lanka
- Joint Exercises and Training: India and Sri Lanka conduct annual defence dialogues to review and accelerate bilateral defence cooperation. Apart from SLINEX (naval exercises) and Mitra Shakti (army exercises), which alternate between the two countries, Sri Lanka also participates in the multilateral naval exercise Milan, hosted by the Indian Navy.
- Capacity Building: A major initiative under India’s grant assistance is the establishment of the Maritime Rescue Coordination Centre (MRCC) for the Sri Lankan Navy, which was inaugurated on June 20, 2024 during the visit of the Indian Foreign Minister.
- The IN Dornier aircraft has been operational for Sri Lanka Air Force since August 2022 for maritime surveillance, conducting successful long-range flights.
- Environmental Cooperation: India has also played a key role as a first responder in preventing large-scale environmental damage, with the Indian Navy and Indian Coast Guard intervening in Sri Lankan waters, such as during the MV Express Pearl in May 2021 and MT New Diamond in September 2020.
- defence Equipment and Supplies: Sri Lanka receives defence equipment and training support from India, making India the largest provider of foreign training assistance to the Sri Lankan Armed Forces.
Indian’s in Sri Lanka:
- Indian-origin Tamils (IOT) are primarily employed in tea and rubber plantations in the Central, Uva, and Sabaragamuwa provinces. A significant number of IOTs residing in Colombo are engaged in business.
- The population of Indian-origin Tamils (IOT) is approximately 1.6 million.
- People of Indian origin (PIOs) in Sri Lanka include Sindhi, Bohra, Gujarati, Memon, Parsi, Malayali, and Telugu speakers, most of whom settled in Sri Lanka after partition and are involved in various business ventures.
- Although their number is relatively small (around 10,000) compared to the IOT population, these PIOs are economically prosperous and hold good positions.
|
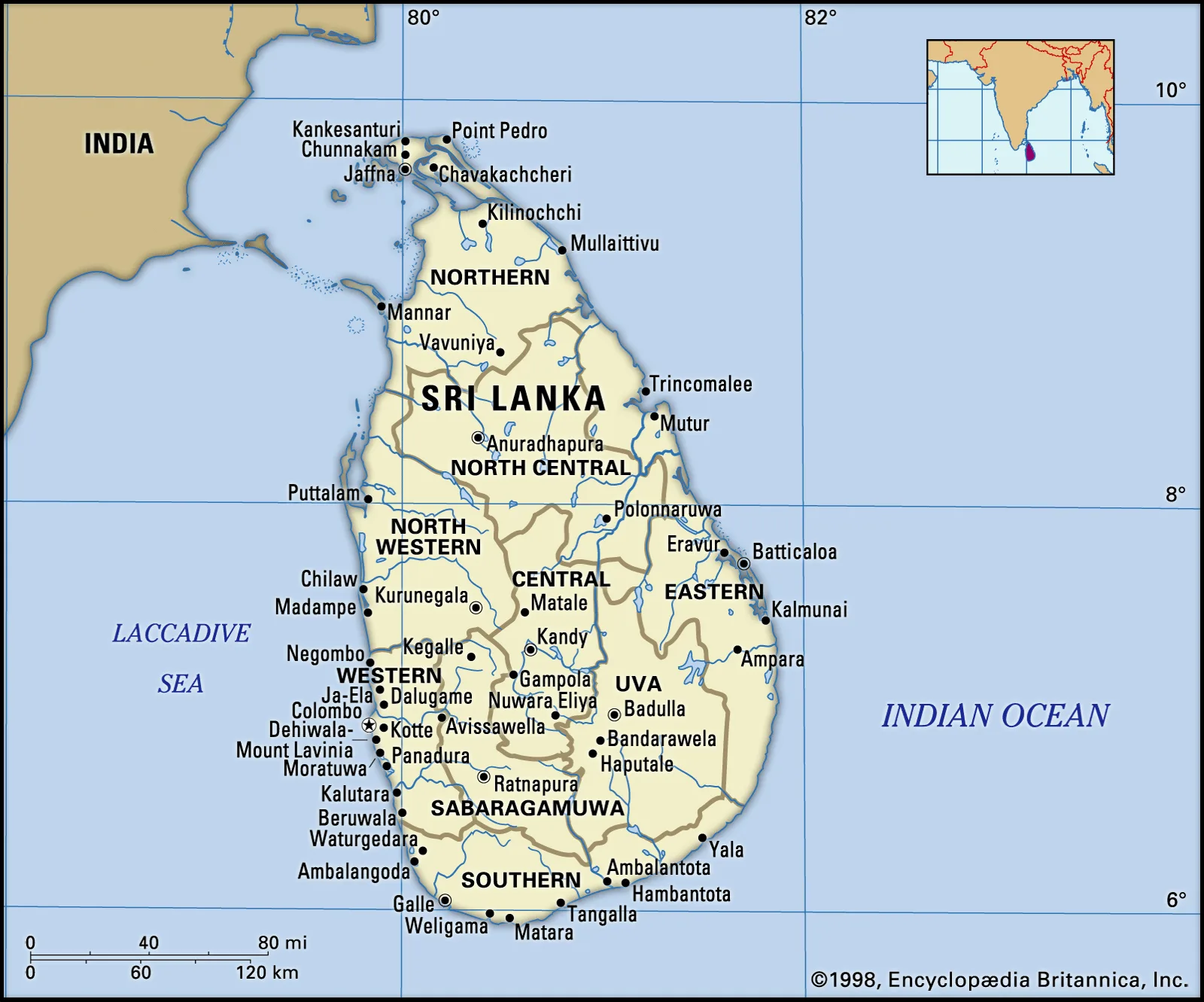
About Sri Lanka:
Image Source: https://www.britannica.com/place/Sri-Lanka
|
Explore our Books: https://apnipathshala.com/product-category/books/
Explore Our test Series: https://tests.apnipathshala.com/