What’s in this Article?
- Table of Contents
- Why in the News?
- What is Agnibaan?
- Importance of the Launch
- 3D Printing
- Rocket Specifications
- Important Facts
- IN-SPACe
- Why in the News?
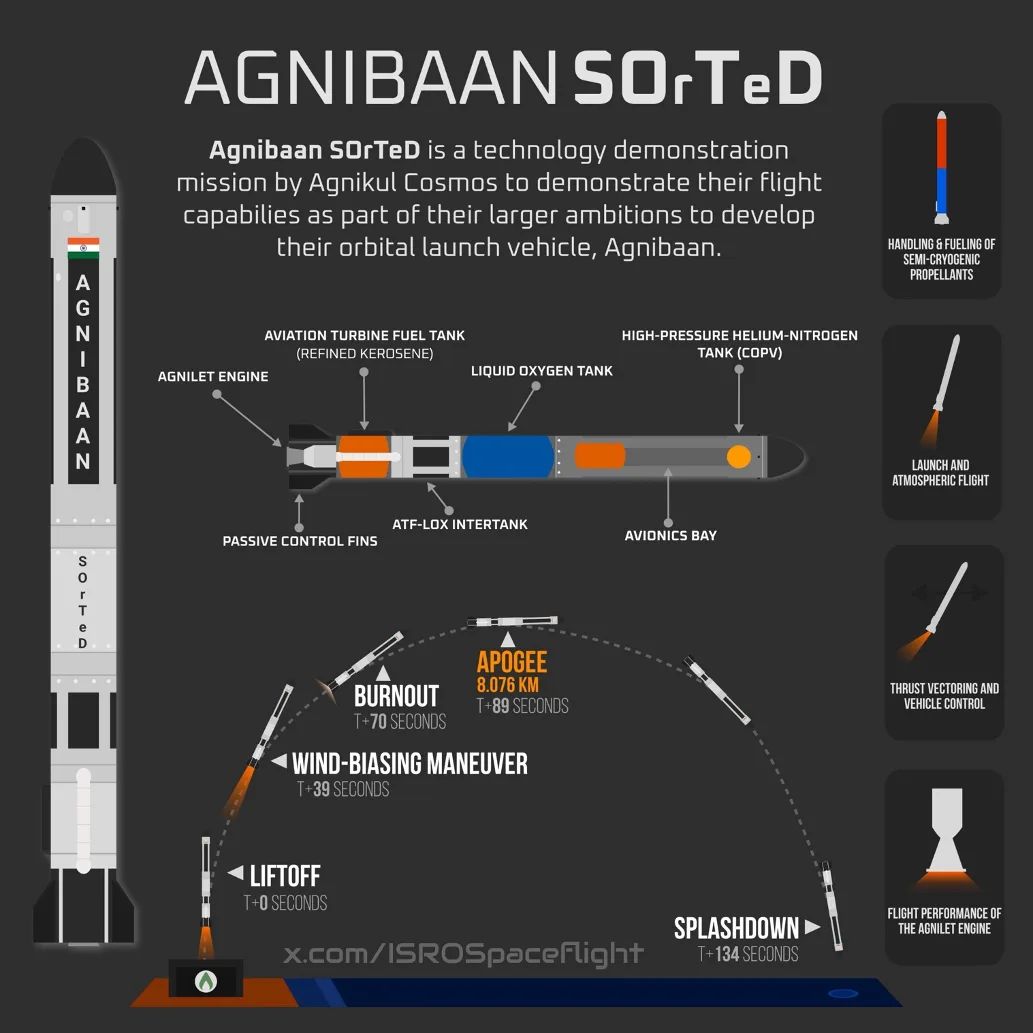
- Chennai-headquartered space start-up Agnikul Cosmos Private Limited launched the world’s first rocket — Agnibaan Sub Orbital Technology Demonstrator (SOrTeD) — with a single piece 3D-printed engine from Sriharikota at 7.15 a.m. on Thursday (May 30, 2024).
- Agnibaan SOrTeD is India’s first launch from a private launchpad, called ‘Dhanush’, established by Agnikul. It is also India’s first semi-cryogenic engine-powered rocket launch and the world’s first single piece 3D-printed engine designed and built indigenously.
- According to details shared by the start-up, the main objective of this mission, which is also the first flight of Agnikul, is to serve as a test flight, showcase home-grown and indigenous technologies, collect critical flight data and ensure optimal To do. Functioning of systems for Agnikul’s orbital launch vehicle, ‘Agnibaan’.
What is Agnibaan?
- Agnibaan is a two-stage rocket with a capacity to carry up to 300 kg to a height of 700 km.
- The rocket engines are powered by liquid oxygen or kerosene.
- It can access both low- and high-inclination orbits and is completely mobile, designed for accessing more than 10 launch ports, as per the company.
- Agnibaan used India’s first semi-cryogenic engine, which uses a mix of liquid and gas for propellant. Liquid propellants can be reused and are safer than solid propellants.
- Semi-cryogenic engines help increase payload capacity, reduce launch costs and improve the overall reliability and performance of the launch vehicles.
- Agnibaan SOrTeD ( SubOrbital Technological Demonstrator) is a suborbital technological demonstrator of the Agnibaan launch vehicle, manufactured by Indian space startup Agnikul Cosmos.
- The SOrTeD mission is a single-stage launch vehicle demonstration that is powered by a semi-cryogenic engine called the Agnilet.
Importance of the Launch
- The launch of Agnibaan SOrTeD is notable for multiple reasons:
- It marks the first launch from a private launchpad in India.
- It represents India’s inaugural launch of a rocket powered by a semi-cryogenic engine.
- It will showcase the world’s first entirely 3D-printed engine, designed and manufactured domestically.
3D Printing
- 3D printing is also known as additive manufacturing which uses materials such as plastics and metals to convert products envisaged on computer-aided design to real three-dimensional items.
It is the opposite of subtractive manufacturing which is cutting out/hollowing out a piece of metal or plastic with, for instance, a milling machine.
Rocket Specifications
- The Agnibaan rocket stands 18 meters tall and has a diameter of 1.3 meters.
- It is capable of carrying a 100-kilogram payload to an altitude of 700 kilometers.
- The rocket uses liquid oxygen (LOX) stored in a cryogenic tank and kerosene as propellants.
- Additionally, it is equipped with a thrust vector controlled, gimballed motor that allows the nozzle to change angles, enabling the thrust to alter the rocket’s flight direction.
Maiden Flight Overview
- Agnibaan’s maiden flight will be sub-orbital, indicating the rocket will not enter space.
- It will launch from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota, India, following a fully guided, vertical ascent.
- Upon reaching an altitude of 10 km, the rocket will start its descent, landing in the Bay of Bengal approximately 30 km from its launch point.
Engine Design
- Agnikul’s rocket features a two-stage configuration.
- The first stage includes a cluster of ‘Agnite’ engines, while the second stage is powered by the ‘Agnilet’ engine.
- Both types of engines are semi-cryogenic, utilizing a mixture of refined kerosene (kept at room temperature) and supercooled liquid oxygen.
- These engines, designed and manufactured by Agnikul in India, are notable for being the world’s first single-piece, 3D-printed engines.
Key Characteristics
- The initial stage of the Agnibaan rocket is adaptable, allowing for the installation of four to seven engines based on the mission’s needs.
- These engines are driven by fuel pumps that use batteries and electric motors for power.
- For secure export and transportation, the rocket is designed without explosives or pyrotechnics, employing pneumatic systems for stage separation instead.
Private Rocket Launch Pad and Mission Control Center
- In November 2022, Agnikul introduced India’s first privately owned rocket launch pad and mission control center, located at the ISRO spaceport in Sriharikota.
- The company is developing a technique to launch rockets from a platform mounted on the back of a truck, offering greater flexibility and mobility than conventional launch systems.
Test Launch Objectives
- The test launch of Agnibaan will include all the avionics, telemetry, and guidance systems typically utilized in its commercial missions.
- The main goal of this test flight is to verify the company’s technology and demonstrate the functionality of the vehicle’s various systems and sub-systems.
Important Facts
- Agnikul Cosmos was established in 2017 by Srinath Ravichandran and Moin SPM, who are both graduates of IIT Madras.
- The company has secured investments from multiple sources, such as pi Ventures, Speciale Invest, and Artha Venture Fund.
- Agnikul Cosmos has partnered with several entities, including the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), the Department of Space (DoS), and the National Centre for Combustion Research and Development.
IN-SPACe (Indian National Space Promotion and Authorisation Centre)
- Nodal Agency: It is a single-window, independent, autonomous agency under the Department of Space (DOS).
- Aim: It is formed following the Space sector reforms to enable and facilitate the participation of private players and acts as an interface between ISRO and Non-Governmental Entities (NGEs) to utilize India’s space resources better.
- Function: IN-SPACe is responsible to promote, enable, authorize and supervise various space activities of non-governmental entities including building launch vehicles & satellites and providing space-based services.
It will enable sharing space infrastructure and premises under the control of DOS/ISRO and establishing of new space infrastructure and facilities.
Explore our courses: https://apnipathshala.com/courses/
Explore Our test Series: https://tests.apnipathshala.com/









