GS Paper II – Government Policies and Interventions, Important aspects of governance GS Paper III – Awareness in the fields of IT, Challenges to internal security through communication networks. basics of cyber security “The fight against internal threats is as important as defending our borders.” – Narendra Modi |
WHY IN NEWS?
Recently, IRCTC has addressed a critical vulnerability on its insurance portal that previously allowed unauthorized access to passengers’ travel details.
This highlights the importance of cybersecurity when we consider the whole digital architecture of India.
What is Cyber Security?
Cyber Security consists of technologies, processes and controls designed to protect systems, networks, programs, devices and data from cyber-attacks.
India is having a rapid pace of digitization across various sectors like education, retail, finance, banking etc. and along with it accompanies more cyber security threats in various forms like –
- Cyber Crime: “Any unlawful act where a computer or communication device or computer network is used to commit or facilitate the commission of the crime”. For example, Hacking, Identity theft, Cyberstalking and fraud.
- Cyber warfare: When a nation-state or international organization attacks and attempts to damage another nation’s computers or information networks through, for example, computer viruses or denial-of-service attacks.
- Cyber spying/cyber espionage: It is the act or practice of obtaining secrets and information without the permission and knowledge of the holder of the information from individuals, competitors, rivals, groups, governments and enemies for personal, economic, political or military advantage using methods on the Internet, networks or individual computers through the use of proxy server.
- Cyber terrorism: It can be defined as the intentional use of computers, networks, and the public internet to cause destruction and harm for personal objectives.
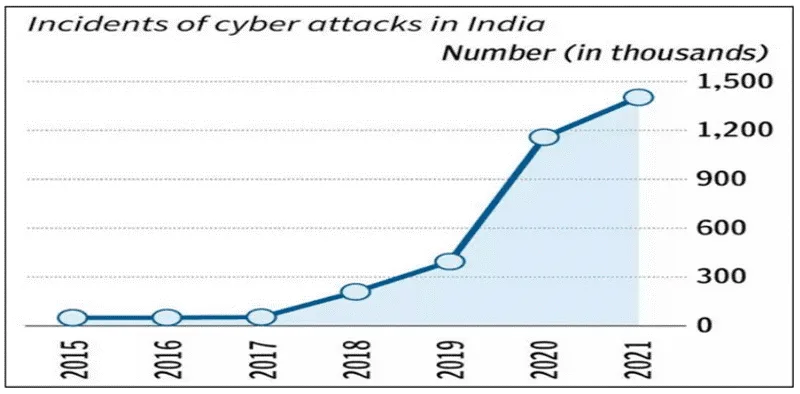
Instances of cybersecurity vulnerabilities :
According to cybersecurity firm Check Point: In 2023, India recorded 2,138 weekly cyber attacks per organization, a 15% increase from 2022. This makes India the second most targeted nation in the Asia Pacific region, after Taiwan.
According to a report by Indusface, India faced over 5 billion cyberattacks, growing 63% every quarter.
- In January 2024, A significant vulnerability that had exposed the personal details of VVIPs, including leading industrialists, celebrities, and sports personalities in the country, was resolved by the Ministry of Corporate Affairs, 10 months after a cybersecurity expert raised the alarm.
- Huge Data Breach from Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR): Regarded as one of the largest data breaches in the country’s history, the personal information of over 81.5 crore Indians was exposed online. This breach, reportedly originating from the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), was highlighted by Resecurity, an American cybersecurity and intelligence firm.
- BSNL Data Breach: Bharat Sanchar Nigam Ltd (BSNL), a major telecom provider, experienced a data breach in which hackers accessed sensitive information, including email addresses, billing details, and contact numbers of thousands of BSNL internet and landline users. Furthermore, crucial data, such as records of mobile service outages and network information, was also compromised.
- RailYatri Data Breach: A substantial amount of data, reportedly hacked from RailYatri, an app sanctioned by the Indian Railway Catering and Tourism Corporation (IRCTC), was listed for sale on the dark web. The compromised information included names, email addresses, mobile phone numbers, and locations of RailYatri users, raising alarm over the security of online platforms that support train travel in India.
- Malware Attack on AIIMS, New Delhi: Cybersecurity systems at the All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) in New Delhi identified a major malware attack. The attempted breach was promptly detected, and the implemented cybersecurity measures successfully mitigated the threat.
METHODS USED FOR CYBER ATTACKS:
Phishing | A fraudulent attempt conducted via email to acquire personal and financial information. |
Cyber Stalking | The repeated use of electronic communication to harass or intimidate an individual. |
Ransomware | A type of malware that encrypts files and storage media on devices like desktops, laptops, and mobile phones, holding the data hostage. The victim is required to pay a ransom to have their device decrypted. |
Whaling | A cyberattack method is where criminals impersonate high-level individuals within an organisation to directly target senior personnel or other key figures, aiming to steal money, or sensitive information, or gain access to computer systems for illicit purposes. |
Spoofing | In cybersecurity, spoofing occurs when an individual or entity pretends to be someone or something else to gain trust, access systems, steal data or money, or distribute malware. |
Botnets | A network of interconnected computers on the Internet that silently disseminate spam, viruses, and malicious content to other Internet devices, following instructions from those controlling the botnet. |
Trojan Horse | A Trojan horse is a destructive program that facades itself as a legitimate application. Unlike viruses, Trojan horses do not replicate themselves but can be equally harmful. They create a backdoor entry into your computer, granting unauthorised users or programs access to your system and allowing for the theft of confidential and personal information.
|
Espionage | Espionage is the practice of acquiring data and information without the owner’s knowledge or consent. |
Pharming | Pharming is a technique employed by phishers to mislead users into thinking they are interacting with a legitimate website. This method utilizes various technical strategies to redirect users to a fraudulent or spoofed website when they enter a valid web address. |
Skimming | Skimming involves extracting data from an unsuspecting user who is not willingly providing the information at that moment. For example, this could occur when someone secretly reads data while in close proximity to a user on public transportation. |
Worms | Worms are malicious programs that continuously replicate themselves on the local drive, network shares, and other connected systems. |
Browser Hijacking | Browser hijacking refers to the unauthorized alteration of a web browser’s settings by malware. The term “hijacking” indicates that these changes occur without the user’s consent. Some instances of browser hijacking can be easily undone, while others may be more challenging to reverse. Various software solutions are available to prevent such modifications. |
Why is Cybersecurity important for India?
- Increasing population of Internet users : India boasts a large and continually growing population of internet users, with approximately 52% of the population currently online. Projections indicate that the number of internet users in India could reach 1 billion by 2027, highlighting the rapid expansion and potential of the digital economy in the nation.
- Expansion of Digital Economy : India’s digital economy is rapidly expanding, encompassing a wide range of sectors, including e-commerce, fintech, health tech, and education. The Indian government has set ambitious targets to further enhance this digital transformation, aiming to position the nation as a global leader in the digital space.
- Increasing role of the service sector : The service sector plays a dominant role in India’s overall GDP, significantly contributing to the nation’s economic growth. Key components of this sector include software exports, business process outsourcing (BPOs), and knowledge process outsourcing (KPOs), which have established India as a global hub for IT and service-based industries.
BPOs and KPOs leverage India’s skilled workforce to provide high-quality services to international clients, further solidifying the sector’s importance in the economy.
Distinct characteristics of cyber warfare in contrast to conventional warfare:
Anonymity of attackers Autonomous battlefield Effective tool for asymmetric warfare Borderless Difficulty in tracing attacks Low expense associated with attacks |
Future conflicts will focus on key areas such as:
Railway traffic control systems Leading institutions in science, technology, and research Defense installations Air traffic management systems Communication networks, including satellites Nuclear facilities Sensitive documents pertaining to internal and external security |
GOVERNMENT INITIATIVES :
- The National Cyber Security Policy, developed by the Department of Electronics and Information Technology (DeitY), serves as a policy framework aimed at protecting both public and private infrastructure from cyber attacks. Additionally, the policy seeks to safeguard various types of information, including personal data of web users, financial and banking information, and sovereign data.
- CERT-In : Indian Computer Emrgency Response Team – It is a nodal agency responsible for handling cyber security threats, such as Phishing and Hacking. It has been operational since 2004 and comes under Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology.
- In a similar vein, the FIN-CERT for India’s financial sector was established to safeguard critical areas of the Indian economy.
- Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C) – The initiative to establish the Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C) was approved in October 2018 to address all forms of cybercrime in a comprehensive and coordinated manner. It comprises seven components:
- National Cyber Crime Threat Analytics Unit
- National Cyber Crime Reporting Portal
- National Cyber Crime Training Centre
- Cyber Crime Ecosystem Management Unit
- National Cyber Crime Research and Innovation Centre
- National Cyber Crime Forensic Laboratory Ecosystem
- Platform for Joint Cyber Crime Investigation Teams.
- The National Cyber Coordination Centre (NCCC) has been established to create essential situational awareness regarding current and potential cybersecurity threats, facilitating timely information sharing to enable proactive, preventive, and protective measures by individual organizations.
- The National Cyber Security Coordinator (NCSC), operating under the National Security Council Secretariat (NSCS), collaborates with various agencies at the national level to address cybersecurity issues.
- The Cyber Surakshit Bharat initiative was designed to raise awareness about cybercrime and enhance the capabilities of Chief Information Security Officers (CISOs) and frontline IT personnel across all government departments. Launched in 2018 by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY), the CISO training represents a pioneering collaboration between the government and an industry consortium under the Public-Private Partnership (PPP) model.
- Defence Cyber Agency (DCyA): The DCyA is a tri-service command within the Indian Armed Forces tasked with addressing cybersecurity threats. It possesses the ability to carry out cyber operations, including hacking, surveillance, data recovery, encryption, and countermeasures against various cyber threat actors.
- The Information Technology Act, of 2000 was enacted to grant legal recognition to electronic communications, electronic commerce, and cyber crimes, among other areas. The IT Act includes deterrent measures designed to address cyber threats and cyber attacks.
OFFENSES UNDER IT ACT 2000:
Section 43 | Data protection refers to laws and regulations that prohibit the storage or sharing of certain types of information or the dissemination of information about individuals without their knowledge or consent. |
Section 66 | Unauthorized access to systems connected to the network. |
Section 66B | Illegally acquiring stolen computer resources. |
Section 69 | Cyberterrorism |
Section 73 | Publishing a false electronic signature certificate with inaccurate details. |
- The National Critical Information Infrastructure Protection Centre (NCIIPC) has been established to safeguard the critical information infrastructure of the country.
- Guidelines have been provided for Chief Information Security Officers (CISOs) outlining their essential roles and responsibilities in securing applications and infrastructure, as well as ensuring compliance.
- Cyber Swachhta Kendra (Botnet Cleaning and Malware Analysis Centre) has been launched for the detection of malicious programs and provides free tools to remove them.
- CERT-In conducts regular training programmes for network/system administrators and Chief Information Security Officers (CISOs) of Government and critical sector organisations regarding securing the IT infrastructure and mitigating cyber attacks.
- Under the Cyber Crime Prevention for Women and Children (CCPWC) Scheme, the Government of India has released grants to States/UTs including Andhra Pradesh for setting up a Cyber Forensic cum Training Laboratory and organizing capacity building programme on cyber awareness and cyber crime investigation. Rs. 4.42 Crore has been released to Andhra Pradesh for the purpose.
- The Indian Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-In) has entered into a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with its overseas counterpart agencies/Computer Emergency Response Teams (CERTs) for information exchange and collaboration for cyber security incident response.
Cooperation in Cyber Security at the International Level :
- Budapest Convention on Cybercrime, 2001: This convention addresses issues such as copyright infringements, computer-related fraud, child pornography, and violations of network security. Its goal is to pursue a unified criminal policy by adopting appropriate legislation and fostering cooperation between international police and judicial systems. India has not yet become a member; currently, the convention has 56 members, including the US and the UK
- Global Centre for Cyber Security : This initiative, launched by the World Economic Forum and headquartered in Geneva, aims to create the first global platform for governments, businesses, experts, and law enforcement agencies to collaborate on cybersecurity challenges and develop a comprehensive regulatory framework.
- Commonwealth Cyber Declaration at the Commonwealth Summit 2018 : Commonwealth Heads of Government committed to the world’s largest inter-governmental agreement on cybersecurity cooperation, which aims to create a cyberspace that supports economic and social development and upholds online rights. It seeks to establish a solid foundation for an effective national cybersecurity response and promote stability in cyberspace through international cooperation. This declaration was signed in April 2018.
- Paris Call : During the UNESCO Internet Governance Forum (IGF) meeting in Paris, “The Paris Call for Trust and Security in Cyberspace” was launched, aiming to establish common principles for securing cyberspace.
WAY FORWARD :
- The IT Act still exhibits gaps and limitations, including unclear definitions, procedures, and penalties for various cyber offences, as well as a low conviction rate for cybercriminals. To effectively tackle these issues, India needs to implement comprehensive and updated laws that encompass all facets of cybersecurity, including cyber terrorism, cyber warfare, cyber espionage, and cyber fraud.
- India has several initiatives and policies to improve its cyber security, such as the National Cyber Security Policy, the Cyber Cells and Cybercrime Investigation Units, the Cyber Crime Reporting Platforms, and the Capacity Building and Training programs.
- Enhancing digital literacy among the population is crucial, as is training personnel in cyber expertise.
- Implementing real-time monitoring and data collection can also thwart cyber-attacks.
- A robust policy, supported by stringent laws, can effectively prevent cyber-attacks in the country.
Explore our courses: https://apnipathshala.com/courses/
Explore Our test Series: https://tests.apnipathshala.com/










2 thoughts on “Challenges in India’s Cybersecurity”
If you are going for most excellent contents like myself,
onpy go to see this site dauly since it offers quality contents, thanks https://Bandurart.Mystrikingly.com/
If yoou are going for most excellent contents likme myself,
only go to ssee this site daily since it offers qquality
contents, thanks https://Bandurart.Mystrikingly.com/
Comments are closed.