Why in News?
In a significant move amid ongoing unrest in Syria, Israel has expanded its control over the Golan Heights. On December 8, 2024, Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu announced that the Israeli Defense Forces (IDF) have deployed military forces in a newly established buffer zone along the Golan Heights.
Introduction to the Golan Heights:
The Golan Heights is a plateau and it is located at the intersection of Syria, Israel, Lebanon, and Jordan in the Middle East. This region, spanning approximately 1,150 square kilometers, has been the focus of longstanding political and military disputes, particularly between Israel and Syria. Originally part of Syria, it was captured by Israel during the Six-Day War of 1967. Since then, it has remained under Israeli control, despite ongoing international disputes and resistance from Syria, which claims the area as part of its sovereign territory.
Source: https://www.britannica.com/place/Golan-Heights
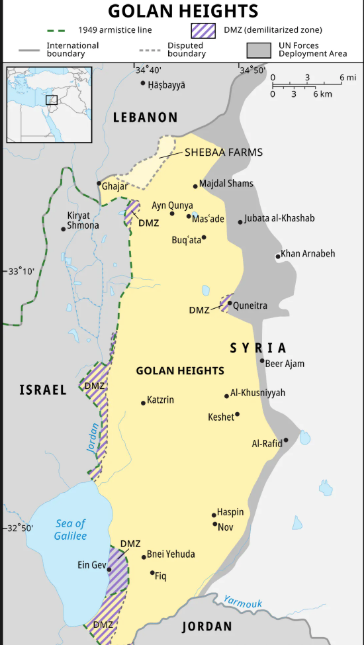
Geography of Golan Heights :
- The Golan Heights is a hilly plateau that rises to over 2,224 metres at its highest point on Mount Hermon.
- The plateau is situated approximately between latitudes 33°N and longitudes 35°45’E.
- It spans about 1,800 square kilometers (700 square miles).
- The Golan Heights lies between the Yarmouk River in the south, the Sea of Galilee and Hula Valley in the west, Mount Hermon in the north, and the Rakkad Valley in the east.
- Highest Point: In 2,814 meters (9,232 feet) highest point is Mount Hermon.
- Lowest Point: The southwestern edge near the Sea of Galilee, at -212 meters (-696 feet).
- The terrain is rocky and mountainous, with fertile land in the south that is suitable for agriculture.
- Physical Characteristics:
- Predominantly volcano with basaltic rock formations.
- Features rugged hills, fertile plains, and elevated plateaus.
- The region includes several important water bodies such as springs, seasonal streams, and rivers.
- The Golan Heights experiences a Mediterranean climate, with hot, dry summers and cool, wet winters.
- The region’s natural features provide both agricultural and military advantages.
- This is critical for surveillance and for the defense of northern Israel. The region also acts as a natural buffer zone, separating Syria from Israel’s densely populated areas.
|
Key Locations within the Golan Heights
|
Historical Context and Background:
- Pre-1967: The Golan Heights has been inhabited and contested for centuries, with Jewish and Arab communities both seeking control over this strategically important region. Following World War I, the area was placed under French Mandate and later became part of independent Syria in 1941. After the 1948 Arab-Israeli War, Syria fortified the Golan Heights, using it as a military position to launch attacks on Israel. Before 1967, the Golan Heights was part of Syria. Syrian forces used the high ground to attack Israeli settlements and towns in the Jordan River Valley and the Sea of Galilee. The area was fortified with military installations.
- The Six-Day War (1967): In 1967, during the Six-Day War, Israel launched a successful military campaign against Syria and captured the Golan Heights. This strategic move gave Israel control over the region’s critical water resources and provided a military advantage with its commanding position over northern Israel. Following the capture, Israel integrated the area into its national framework, establishing settlements and military bases.
- The Yom Kippur War (1973): In 1973, Syria tried to recapture this area, although Syria made initial gains, Israel ultimately repelled the Syrian forces and maintained control over the region. The war led to renewed peace talks, but a final resolution to the dispute has remained elusive.
Significance of Golan height:
- Strategic Location: The Golan Heights overlooks northern Israel, southern Syria, and parts of Lebanon and Jordan, making it a key point for monitoring and controlling regional movements.
- Military Advantage: Its elevated terrain provides a natural defense and a vantage point for surveillance, giving the occupying force an upper hand in military operations.
- Water Resources: The region is a critical source of water, feeding into the Jordan River and the Sea of Galilee, which are vital for Israel’s water supply.
- Agriculture: The fertile soil of the Golan Heights supports agriculture, including vineyards and orchards.
- Tourism and Settlements: The area has become a hub for tourism and Israeli settlements, with its scenic landscapes and historical significance attracting visitors.
Disputed Ownership and Legal Status:
- The UN Security Council Resolution 242, adopted after the Six-Day War, called for Israel’s withdrawal from territories captured during the conflict, including the Golan Heights. However, Israel’s control over the region has not been recognized by most of the international community, which views the Golan as Syrian territory under occupation.
- In 1981, Israel passed the Golan Heights Law, which effectively annexed the region and extended Israeli law to the area. This move was met with widespread international condemnation, and most countries, including the European Union, refused to recognize Israel’s sovereignty over the Golan.
- In 2019 the United States officially recognized Israeli sovereignty over this area. This was a controversial move, as it contradicted the longstanding international consensus on the issue.
- The Golan Heights remains a central issue in the Israeli-Syrian peace process. Despite numerous negotiations and peace efforts, the dispute over the Golan continues, with no resolution in sight.
The Golan Heights Today: Israeli Settlements and Military Presence
- Since 1967 the region has seen significant demographic changes as Israeli settlers have moved into the area, while the Syrian Druze population has been largely marginalized.
- Israel maintains a significant military presence in the Golan Heights, including military bases and defense installations. The region serves as a buffer zone between Israel and Syria, providing a strategic advantage in the event of conflict.
- The local Druze community, who are ethnically Syrian, have faced challenges in the Golan. Many Druze rejected Israeli citizenship. Their rights and status in the region remain a sensitive issue, as they navigate the complex political landscape.
The Future of the Golan Heights:
- Challenges to a Resolution of the Golan Heights Dispute: The Golan Heights remains one of the most difficult issues in the Israeli-Syrian conflict. Both sides have deeply entrenched positions, with Syria demanding the return of the Golan Heights, while Israel insists on maintaining control for security reasons.
- The Influence of Regional Powers and Global Politics on the Dispute: The United States, Russia, and other regional powers, such as Iran and Turkey, influence the dispute. Their involvement in the broader Middle East conflicts, along with competing interests, makes a long-term resolution more challenging.
|
Historic and Archaeological Treasures of the Golan Heights: The Golan Heights is rich in archaeological and historical significance, featuring numerous ancient sites, mountains, rivers, and waterfalls.
|
Explore our Books: https://apnipathshala.com/product-category/books/
Explore Our test Series: https://tests.apnipathshala.com/