GS Paper-II: Government policies and interventions GS Paper-III: Environmental Pollution and Degradation, Conservation |
Why in the News?
The Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) has exempted export-oriented green hydrogen projects from its approved list of domestic solar module manufacturers. This move aims to help green hydrogen projects reduce costs to be competitive with grey hydrogen.
What’s in Today’s Article?
- Overview of Hydrogen (Properties, Abundance)
- Types of Hydrogen (Grey, Blue, Green)
- Insights on Green Hydrogen (Benefits, India’s Goals, Applications, Challenges, etc.)
- News Summary (SIGHT Program)
About Hydrogen:
- Hydrogen is the lightest chemical element.
- It is colourless, odourless, tasteless, non-toxic, and highly flammable.
- It is the third most abundant element in the human body, after oxygen and carbon.
- Hydrogen is the most abundant chemical substance in the universe, making up about 75% of all normal matter.
- It can be produced from various resources, including fossil fuels, nuclear energy, biomass, and renewable energy sources.
Types of Hydrogen:
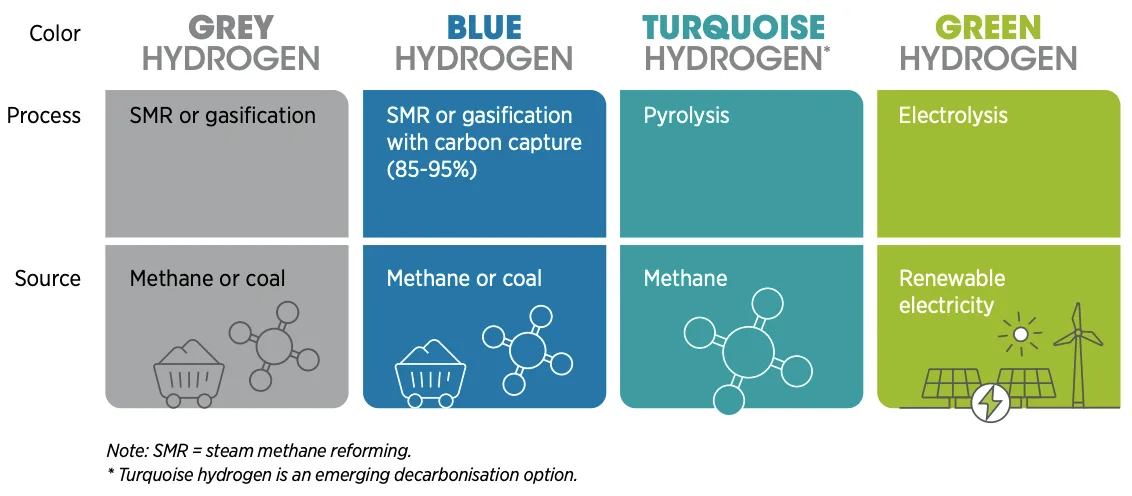
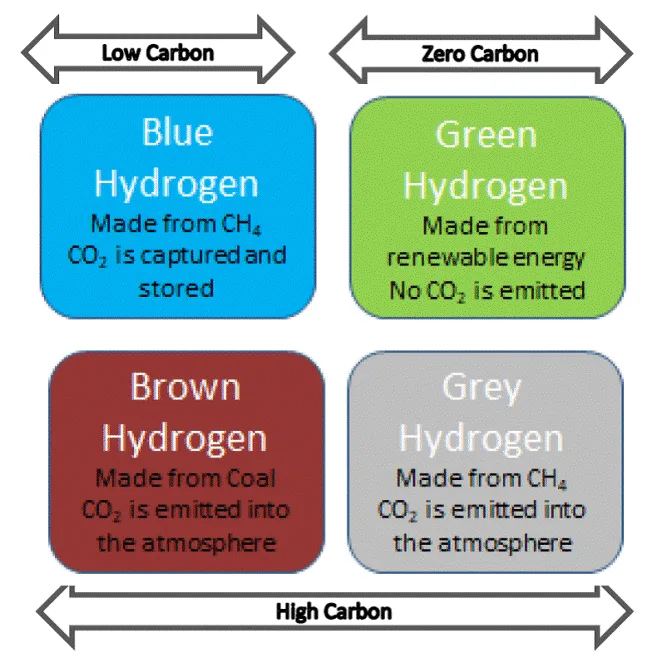
Grey Hydrogen:
- Grey hydrogen is produced from natural gas or methane through a process called Steam Methane Reformation (SMR), without capturing the greenhouse gases generated in the process.
- In SMR, high-temperature steam (700°C–1,000°C) is used to extract hydrogen from a methane source, such as natural gas.
- The CO2 generated during this process is released directly into the atmosphere.
- Unfortunately, grey hydrogen accounts for about 95% of the hydrogen produced globally today.
Blue Hydrogen:
- Blue hydrogen is produced through steam reforming, but unlike grey hydrogen, the carbon emissions generated are captured and stored underground using industrial carbon capture and storage (CCS) technology.
- This type of hydrogen is often considered carbon neutral because the emissions are not released into the atmosphere.
- However, some argue that it should be described as “low carbon” rather than carbon neutral, as 10-20% of the carbon produced cannot be captured.
- Blue hydrogen offers significant cost and emissions advantages over other forms of hydrogen production.
Green Hydrogen:
- Green hydrogen is generated using renewable energy sources, like solar or wind power, to split water into hydrogen and oxygen through electrolysis.
- This method makes green hydrogen the cleanest option since it produces hydrogen without any CO2 emissions as a by-product.
- Although it currently accounts for only about 0.1% of total hydrogen production, its share is expected to grow as the cost of renewable energy continues to decrease.
Applications of Green Hydrogen
Agriculture Sector:
- Green Hydrogen as an Alternative to Fossil Fuels in Agriculture:
- Green hydrogen has the potential to replace traditional fertilizers by producing ammonia using renewable energy sources. Currently, ammonia is made using natural gas, a fossil fuel that emits greenhouse gases. Green ammonia, made from green hydrogen, is carbon-free and offers other benefits over traditional fertilizers, such as improved efficiency and reduced soil acidity. However, scaling up green ammonia production requires significant investment in infrastructure and new technologies, as it is currently more expensive than conventional methods.
- Green Hydrogen-Powered Farm Machinery:
Farm machinery like tractors, harvesters, and irrigation systems are energy-intensive. Green hydrogen can power this machinery, significantly reducing greenhouse gas emissions while still meeting energy needs for essential farming tasks. - Green Hydrogen for Water Management:
Green hydrogen can power desalination plants, converting saltwater into freshwater, thus reducing dependence on scarce freshwater resources and supporting sustainable agriculture.
Transport Sector:
- Hydrogen Fuel Cells:
Hydrogen fuel cells convert hydrogen and oxygen into electricity, water, and heat, making them a zero-emission power source. Vehicles powered by hydrogen fuel cells have a longer range than battery electric vehicles and can be refueled in minutes, making them a convenient alternative for long-distance travel.
Industrial Sector:
- Cost Savings:
Green hydrogen can be produced using excess renewable energy during off-peak hours. This green hydrogen can be stored and used when energy demand is high, helping to reduce costs and support sustainable development. - Reliability:
Green hydrogen can be produced and stored on-site, providing a consistent and reliable energy source for industrial processes, which can reduce dependence on the electricity grid and promote energy independence. - Waste Reduction:
Green hydrogen can be produced from waste materials, such as municipal solid waste and agricultural waste, contributing to waste reduction and sustainable development. - Increased Energy Efficiency:
Green hydrogen can power fuel cells, which are more energy-efficient than traditional combustion engines, helping to lower energy consumption and enhance overall efficiency.
India’s Green Hydrogen Production Goals Compared to Other Countries:
- In August 2021, Prime Minister Narendra Modi launched the National Hydrogen Mission, aiming to bolster environmental security and establish India as a global leader in the production and export of green hydrogen.
- India aims to produce 5 million tonnes of green hydrogen annually by 2030, which is half of the European Union’s target of 10 million tonnes by the same year.
- In contrast, China has set a shorter-term goal to produce up to 200,000 tonnes of green hydrogen annually by 2025.
- Spain, Germany, and France have set their targets to install 4 GW, 5 GW, and 6.5 GW of green hydrogen capacity respectively by 2030.
Current Capacity:
- India currently has 26 hydrogen projects with a combined capacity of 255,000 tonnes per year.
- Only about 8,000 tonnes per year of capacity is expected to become operational by 2024.
Challenges in Green Hydrogen Implementation
- Cost:
Currently, green hydrogen is more expensive than traditional fossil fuels. Its production, storage, and distribution require specialized equipment and infrastructure, adding to the cost. - Infrastructure:
For green hydrogen to become widely adopted, a comprehensive infrastructure for its production, storage, and distribution needs to be established. This infrastructure must integrate with existing energy systems to support a smooth transition to green hydrogen. - Energy Storage:
Green hydrogen production relies on intermittent renewable energy sources such as wind, solar, and hydro power, which can fluctuate. Effective energy storage solutions are essential to ensure a consistent supply of green hydrogen. Technologies like batteries and hydrogen storage can help manage and store excess renewable energy. - Safety:
Green hydrogen is highly flammable and requires careful handling and storage. Developing and implementing stringent safety protocols and regulations is vital to ensure its safe use. - Public Acceptance:
Gaining public acceptance is crucial for the widespread adoption of green hydrogen. Educating the public about its benefits and its role in combating climate change is necessary to build support for green hydrogen initiatives.
Exemptions for Export-Oriented Green Hydrogen Projects:
- The Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) has granted exemptions to export-oriented green hydrogen projects from its Approved List of Models and Manufacturers (ALMM), which typically requires the use of domestically produced solar modules.
- This exemption allows these projects to use less expensive imported modules, thereby significantly lowering production costs and improving competitiveness against grey hydrogen.
- The goal of this exemption is to boost global demand for green hydrogen, aligning with India’s focus on increasing exports. India aims to produce 5 million metric tons of green hydrogen by 2030, with projects already planned for 7.5 MMT.
- Additionally, MNRE has allocated Rs 17,490 crore for electrolyser manufacturing and green hydrogen capacity under its SIGHT program, and Rs 400 crore for R&D initiatives.
- Other incentives include the waiver of transmission charges and environmental clearance requirements for green hydrogen projects.
About the SIGHT Program:
- The SIGHT (Strategic Interventions for Green Hydrogen Transition) program is a Government of India initiative designed to encourage the production and adoption of green hydrogen within the country.
Key Features Include:
- Electrolyser Manufacturing Focus: The program aims to enhance domestic production of electrolysers, crucial for generating green hydrogen from renewable energy sources.
- Green Hydrogen Production: It promotes the development of green hydrogen production facilities in India, striving to position the country as a global leader in green hydrogen exports.
- Financial Allocation: The government has earmarked Rs 17,490 crore for the SIGHT program, providing financial support to encourage investment in electrolyser manufacturing, green hydrogen projects, and related infrastructure.
- Employment and Investment Boost: The program is expected to generate job opportunities and attract both domestic and international investments in clean energy technologies.
- Incentives and Policy Support: It offers incentives such as exemption from transmission charges for green hydrogen projects and funding for research and development (R&D).
Explore our courses: https://apnipathshala.com/courses/
Explore Our test Series: https://tests.apnipathshala.com/