|
GS Paper III: India and Its Neighbors, Bilateral Groupings, and Agreements |
Why in News?
India-Mauritius Relations: Recently, the Prime Minister of India visited Mauritius. During this visit, both countries presented a vision for an enhanced strategic partnership. They signed eight important agreements on trade, maritime security, and defense cooperation. The Prime Minister received Mauritius’ highest civilian award, the ‘Grand Commander of the Order of the Star and Key of the Indian Ocean’.
Key Highlights of Mauritius Visit 2025
- Defense and Maritime Security Cooperation
- India helped Mauritius strengthen its maritime security and protect its large Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ).
- Both countries agreed on joint maritime surveillance, hydrographic surveys, and defense equipment supply.
- India assisted in building a new airstrip and jetty on Agaléga Island, and both sides agreed to continue the project.
- They finalized amendments to the Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement (DTAA) to align with international tax standards.
- India launched the “MAHASAGAR Vision”, a strategy to strengthen ties with the Indian Ocean region and other maritime nations.
- Infrastructure Projects
- India made a significant contribution to Mauritius’ infrastructure and social development.
- Major completed projects include the Metro Express Project, a new ENT hospital, and 956 social housing units.
- India approved 100 electric buses, a charging network, a 100 km water pipeline replacement, and a new Parliament building.
- India will provide financial support for the redevelopment of Ganga Talao, a major spiritual site.
- The President of Mauritius inaugurated the Atal Bihari Vajpayee Public Service and Innovation Institute, a health center, and 20 Indian-funded community projects.
- Space and Climate Change Cooperation
- India and Mauritius will jointly develop a satellite to help Mauritius with weather forecasting, disaster management, and maritime security.
- Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) will train Mauritian scientists.
- Under the QUAD framework, India will provide Mauritius with a modern Earth observation system to monitor climate change.
- Health and Education Cooperation
- India launched Jan Aushadhi centers in Mauritius to provide affordable medicines.
- India will assist in setting up a digital health office system to improve Mauritius’ healthcare services.
- Both countries will work on a science and technology strategy and help establish the National Directorate of Science and Technology in Mauritius.
- Economic and Trade Cooperation
- India and Mauritius will simplify trade in local currencies (Indian Rupee and Mauritian Rupee).
- They agreed to increase investment in new sectors, including the ocean economy, pharmaceuticals, IT, and fintech.
- Both nations will further strengthen bilateral trade under the CECPA Agreement (Comprehensive Economic Cooperation and Partnership Agreement).
|
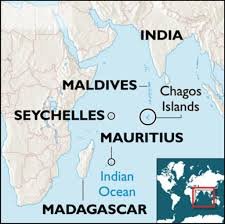
About Mauritius
|
India-Mauritius Relations: Historical, Cultural, and Strategic Partnership
- Historical Background and Cultural Ties
-
- From 1834 to 1900, around 500,000 Indian indentured laborers were brought to Mauritius under British rule. About two-thirds settled permanently.
- Before this, in the 18th century, French colonizers brought artisans and masons from Puducherry to Mauritius.
- India and Mauritius established diplomatic relations in 1948, even before Mauritius gained independence in 1968.
- In 1901, Mahatma Gandhi visited Mauritius and advocated for education and political empowerment of the Indian community.
- To honor Gandhi’s legacy, March 12, the day of India’s Dandi March, was declared Mauritius’ National Day.
- Today, about 70% of Mauritius’ population is of Indian origin.
- Institutions like Mahatma Gandhi Institute (MGI), World Hindi Secretariat, and Indira Gandhi Cultural Centre (IGCIC) work to preserve Indian culture, language, and traditions.
-
- Economic and Trade Cooperation
- India-Mauritius bilateral trade reached $851.13 million in 2023-24.
- In 2021, India signed the Comprehensive Economic Cooperation and Partnership Agreement (CECPA), its first trade agreement with an African country.
- In 2023-24, Mauritius was India’s second-largest FDI source, investing $7.97 billion.
- Since 2000, Mauritius has contributed $175 billion in FDI to India, about 25% of total FDI inflows.
- However, FDI inflows declined after the 2016 amendment to the Double Tax Avoidance Agreement (DTAA).
- Defense and Maritime Cooperation
- India considers Mauritius the “Guardian of the Western Indian Ocean”.
- In 2025, both countries signed an agreement to share White Shipping Information to enhance maritime security.
- The Agaléga Island Project (2024), funded by India, includes an airstrip and jetty construction to strengthen security and disaster management in Mauritius.
- Other Areas of Cooperation
- In 1986, ISRO established a Telemetry, Tracking, and Telecommand Station in Mauritius.
- In 2023, ISRO and Mauritius Research and Innovation Council (MRIC) agreed to develop a joint satellite project.
- Mauritius is a key beneficiary of the Indian Technical and Economic Cooperation (ITEC) program.
- Since 2007, over 4,868 Mauritian professionals have been trained in India.
- Since 2004, Mauritius has allowed visa-free travel for Indians, promoting tourism and cultural exchange.
- Currently, Mauritius has 17,403 Indian citizens and 11,600 OCI cardholders.
- People of Mauritian-Indian origin can get OCI cards for up to seven generations.
Significance of India-Mauritius Bilateral Relations
- Geopolitical and Maritime Strategy: Mauritius is a key strategic partner due to its location in the Indian Ocean. It plays a crucial role in India’s SAGAR (Security and Growth for All in the Region) vision. With an Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) of 2.3 million sq. km, Mauritius helps maintain regional balance and counters external influences.
- India’s Gateway to Africa: Mauritius is part of the African Continental Free Trade Agreement (AfCFTA). This makes Mauritius a gateway for India’s trade and investment in Africa. Mauritius is India’s second-largest FDI source after Singapore.
- India’s Development Assistance: Since 1968, India has provided over $1.1 billion in development aid to Mauritius. India has supported major projects like: Metro Express Project, Supreme Court Building, Hospital Construction, Social Housing Projects. These projects strengthen infrastructure and promote sustainable development in Mauritius.
- Administrative Training and Capacity Building: Under the ITEC program, 4,940 Mauritian professionals have been trained since 2002. India’s National Centre for Good Governance (NCGG) provides customized training for Mauritian civil servants, improving governance and efficiency.
- Regional Cooperation: Mauritius is a member of the Colombo Security Conclave (CSC), along with India, Sri Lanka, Maldives, and Bangladesh. This promotes maritime security and regional collaboration in the Indian Ocean. Mauritius is also part of India’s Information Fusion Centre – Indian Ocean Region (IFC-IOR), improving monitoring of maritime trade routes.
|
UPSC Previous Year Questions (PYQs) Question (2015): Consider the following statements regarding the Indian Ocean Rim Association for Regional Cooperation (IOR-ARC):
Which of the above statements is/are correct? Answer: (d) Question (2010): A large share of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) in India comes from Mauritius, compared to major economies like the UK and France. What is the reason? (a) India gives priority to some countries for FDI inflows. Answer: (b) |
Explore our Books: https://apnipathshala.com/product-category/books/
Explore Our test Series: https://tests.apnipathshala.com/