What’s in this Article?
- Global Presence:
- S&P Global operates in multiple countries around the world, providing a broad range of financial information services to a diverse client base, including financial institutions, corporations, governments, and educational institutions.
- Global Presence:
- Market Influence:
- The company’s credit ratings and benchmarks are widely used by investors and other market participants to assess risk and performance, making S&P Global a critical player in the global financial ecosystem.
- Vision and Mission:
- S&P Global aims to provide essential intelligence that helps individuals and organizations make informed decisions with conviction, thus fostering growth and progress in global markets.
Disclaimer: The article may contain information pertaining to prior academic years; for further information, visit the exam’s “official or concerned website”.
Explore our courses: https://apnipathshala.com/courses/
Explore Our test Series: https://tests.apnipathshala.com/
- Global Presence:
- S&P Global operates in multiple countries around the world, providing a broad range of financial information services to a diverse client base, including financial institutions, corporations, governments, and educational institutions.
- Global Presence:
- Market Influence:
- The company’s credit ratings and benchmarks are widely used by investors and other market participants to assess risk and performance, making S&P Global a critical player in the global financial ecosystem.
- Vision and Mission:
- S&P Global aims to provide essential intelligence that helps individuals and organizations make informed decisions with conviction, thus fostering growth and progress in global markets.
Disclaimer: The article may contain information pertaining to prior academic years; for further information, visit the exam’s “official or concerned website”.
Explore our courses: https://apnipathshala.com/courses/
Explore Our test Series: https://tests.apnipathshala.com/
- Key Services and Divisions:
- S&P Global Ratings: One of the world’s largest credit rating agencies, providing credit ratings for sovereign, corporate, and municipal entities.
- S&P Global Market Intelligence: Offers data, analytics, and research covering a wide range of financial instruments and industries.
- S&P Dow Jones Indices: Manages some of the most well-known market indices, including the S&P 500.
- S&P Global Platts: Provides information and benchmarks for the energy and commodities markets.
- History and Background:
- Founded: 1860
- Headquarters: New York City, New York, USA
- Evolution: Initially known as The McGraw-Hill Companies, it rebranded to S&P Global Inc. in 2016 to reflect its core focus on financial information and analytics.
- Global Presence:
- S&P Global operates in multiple countries around the world, providing a broad range of financial information services to a diverse client base, including financial institutions, corporations, governments, and educational institutions.
- Global Presence:
- Market Influence:
- The company’s credit ratings and benchmarks are widely used by investors and other market participants to assess risk and performance, making S&P Global a critical player in the global financial ecosystem.
- Vision and Mission:
- S&P Global aims to provide essential intelligence that helps individuals and organizations make informed decisions with conviction, thus fostering growth and progress in global markets.
Disclaimer: The article may contain information pertaining to prior academic years; for further information, visit the exam’s “official or concerned website”.
Explore our courses: https://apnipathshala.com/courses/
Explore Our test Series: https://tests.apnipathshala.com/
- A sovereign credit rating evaluates a country’s ability to fulfill its financial commitments, reflecting its creditworthiness.
- It gauges the credit risk linked to the nation’s bonds or other debt instruments.
- This rating is provided by agencies like Standard & Poor’s, Moody’s, and Fitch Ratings.
- India’s current ratings
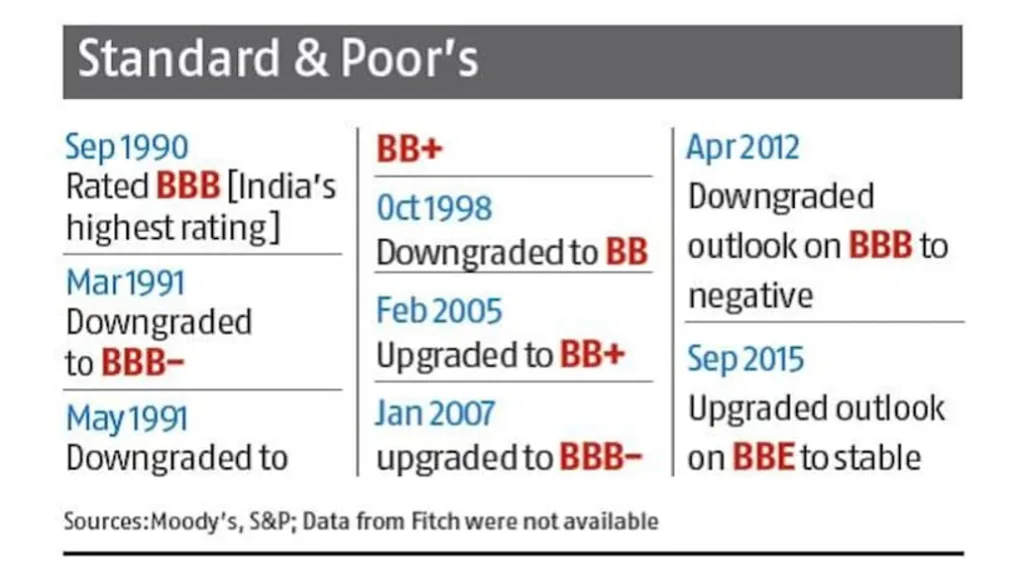
- S&P and Fitch rate India ‘BBB-‘ and Moody’s ‘Baa3’, all indicative of the lowest-possible investment grade, but with a stable outlook.
- What does BBB mean?
- A ‘BBB’ rating indicates that expectations of default risk are currently low.
The capacity for payment of financial commitments is considered adequate, but adverse business or economic conditions are more likely to impair this capacity.
- What is a Rating Agency?
- Rating agencies evaluate the creditworthiness or potential of a country, equity, or debt. Investors use their reports to make informed decisions about investing in specific countries or companies within those regions.
- The agencies determine the financial stability and default risk of these entities. Essentially, these reports assist investors in determining the likelihood of receiving a return on their investment.
- What do they do?
- The agencies periodically re-evaluate previously assigned ratings after new developments geopolitical events or a significant economic announcement by the concerned entity.
- Their reports are sold and published in financial and daily newspapers.
- What grading system do they use?
- The three leading credit rating agencies, namely Standard & Poor’s, Moody’s, and Fitch, adhere to largely similar grading systems.
- Standard & Poor’s assigns its highest grade, AAA, to entities—be they countries, equities, or debts—with an extremely high ability to fulfill their financial obligations.
- Its grading scale includes letters A, B, and C, with the possibility of appending a single or double letter to indicate a higher grade.
- Moody’s categorizes ratings into short and long-term classifications. Its long-term ratings span from Aaa to C, with Aaa being the most favorable.
- Similarly, Fitch rates from AAA to D, with D representing the lowest rating. It employs the same sequence as Moody’s and Standard & Poor’s.
- The importance of such evaluations
- Access to Funding: Enhanced credit ratings enable nations to secure funding at reduced expenses, while lower ratings imply higher borrowing costs.
- Investment Analysis: Investors utilize credit ratings to gauge a nation’s creditworthiness and evaluate investment risks associated with it.
- Economic Advancement: Elevated credit ratings typically result in heightened foreign investments, fostering job creation, enhancing productivity, and driving economic progress.
- Global Commerce: Nations with superior credit ratings are perceived as more dependable and credible, making them preferred trading allies for other nations.
- Public Image: Nations with inferior credit ratings may be perceived as less dependable or steady, potentially undermining diplomatic ties and political sway.
- Critique of rating agencies
- Credibility: Well-known rating agencies openly disclose their methodology, relying on publicly accessible macroeconomic data from countries to bolster the trustworthiness of their assessments.
- Bias: These agencies faced significant backlash, accused of contributing to the onset of the U.S. financial crisis starting in 2007.
- Misleading metrics: They miscalculated the credit risk linked with structured credit products and were slow to adapt their ratings to worsening market conditions.
- Inaccurate: Allegations of methodological flaws and conflicts of interest were leveled against them repeatedly.
- Future Growth Prospects
- According to assessments by rating agencies, the nation is projected to experience a 7% annual growth rate if it continues on its current growth path and implements the outlined policy measures.
- This growth trajectory is anticipated to subsequently alleviate the government’s debt-to-GDP ratio.
- Over the past three years, real GDP growth has averaged 8.1% annually, the highest among nations in the Asia-Pacific region.
- The analysis also indicates the potential for the government to reduce its fiscal deficit, with the share expected to decrease from 7.9% of GDP in fiscal 2025 to 6.8% by fiscal 2028.
- The rating agency suggests that it may reconsider the country’s rating within the next 24 months if a prudent fiscal and monetary approach is adopted, focusing on reducing the government’s high debt and interest obligations while bolstering economic resilience.
- S&P stated, “Taking such cautious fiscal and monetary steps to address the government’s significant debt and interest burden while enhancing economic resilience could result in an improved rating over the next 24 months.”
About S&P Global Inc.
- S&P Global Inc. is a leading provider of financial information and analytics. The company delivers essential intelligence that powers decision-making in various sectors such as finance, business, and government. Its services include credit ratings, benchmarks, analytics, and data solutions, which are crucial for financial market participants to make informed decisions.
- Key Services and Divisions:
- S&P Global Ratings: One of the world’s largest credit rating agencies, providing credit ratings for sovereign, corporate, and municipal entities.
- S&P Global Market Intelligence: Offers data, analytics, and research covering a wide range of financial instruments and industries.
- S&P Dow Jones Indices: Manages some of the most well-known market indices, including the S&P 500.
- S&P Global Platts: Provides information and benchmarks for the energy and commodities markets.
- History and Background:
- Founded: 1860
- Headquarters: New York City, New York, USA
- Evolution: Initially known as The McGraw-Hill Companies, it rebranded to S&P Global Inc. in 2016 to reflect its core focus on financial information and analytics.
- Global Presence:
- S&P Global operates in multiple countries around the world, providing a broad range of financial information services to a diverse client base, including financial institutions, corporations, governments, and educational institutions.
- Global Presence:
- Market Influence:
- The company’s credit ratings and benchmarks are widely used by investors and other market participants to assess risk and performance, making S&P Global a critical player in the global financial ecosystem.
- Vision and Mission:
- S&P Global aims to provide essential intelligence that helps individuals and organizations make informed decisions with conviction, thus fostering growth and progress in global markets.
Disclaimer: The article may contain information pertaining to prior academic years; for further information, visit the exam’s “official or concerned website”.
Explore our courses: https://apnipathshala.com/courses/
Explore Our test Series: https://tests.apnipathshala.com/
- Inshort
- In a recent development S&P Global, the premier rating agency has changed India’s Sovereign rating outlook from stable to positive after a gap of 14 years.
- Major fiscal reforms and appropriate public spending stand as pillars of this development.
- However, the rating agency has retained the sovereign rating at the lowest investment grade ‘BBB-‘.
- In Depth
- In a statement issued on Wednesday, the US-based agency indicated that India’s rating might be upgraded within the next 24 months. This potential upgrade hinges on the country adopting prudent fiscal and monetary policies aimed at reducing the government’s substantial debt and interest expenses, while also bolstering its economic resilience. This rating update follows closely on the heels of the RBI’s release of a 2.10 lakh crore dividend to the government, intended to help bridge the fiscal deficit.
- S&P reported, “India’s outlook has been revised to positive due to strong growth and improved quality of government spending; BBB- long-term and ‘A-3’ short-term unsolicited foreign and local currency sovereign credit ratings are affirmed.”
- The agency highlighted that India’s vigorous economic growth is positively impacting its credit metrics. “We anticipate that sound economic fundamentals will support growth momentum over the next two to three years. Regardless of election outcomes, we expect a general continuity in economic reforms and fiscal policies,” S&P stated.
- “Our positive outlook on India is based on its strong economic growth, significant improvements in the quality of government spending, and a political commitment to fiscal consolidation. We believe these elements are coming together to enhance credit metrics,” S&P added.
- In Depth
- What are Sovereign Credit Ratings?
- A sovereign credit rating evaluates a country’s ability to fulfill its financial commitments, reflecting its creditworthiness.
- It gauges the credit risk linked to the nation’s bonds or other debt instruments.
- This rating is provided by agencies like Standard & Poor’s, Moody’s, and Fitch Ratings.
- India’s current ratings
- S&P and Fitch rate India ‘BBB-‘ and Moody’s ‘Baa3’, all indicative of the lowest-possible investment grade, but with a stable outlook.
- What does BBB mean?
- A ‘BBB’ rating indicates that expectations of default risk are currently low.
The capacity for payment of financial commitments is considered adequate, but adverse business or economic conditions are more likely to impair this capacity.

- What is a Rating Agency?
- Rating agencies evaluate the creditworthiness or potential of a country, equity, or debt. Investors use their reports to make informed decisions about investing in specific countries or companies within those regions.
- The agencies determine the financial stability and default risk of these entities. Essentially, these reports assist investors in determining the likelihood of receiving a return on their investment.
- What do they do?
- The agencies periodically re-evaluate previously assigned ratings after new developments geopolitical events or a significant economic announcement by the concerned entity.
- Their reports are sold and published in financial and daily newspapers.
- What grading system do they use?
- The three leading credit rating agencies, namely Standard & Poor’s, Moody’s, and Fitch, adhere to largely similar grading systems.
- Standard & Poor’s assigns its highest grade, AAA, to entities—be they countries, equities, or debts—with an extremely high ability to fulfill their financial obligations.
- Its grading scale includes letters A, B, and C, with the possibility of appending a single or double letter to indicate a higher grade.
- Moody’s categorizes ratings into short and long-term classifications. Its long-term ratings span from Aaa to C, with Aaa being the most favorable.
- Similarly, Fitch rates from AAA to D, with D representing the lowest rating. It employs the same sequence as Moody’s and Standard & Poor’s.
- The importance of such evaluations
- Access to Funding: Enhanced credit ratings enable nations to secure funding at reduced expenses, while lower ratings imply higher borrowing costs.
- Investment Analysis: Investors utilize credit ratings to gauge a nation’s creditworthiness and evaluate investment risks associated with it.
- Economic Advancement: Elevated credit ratings typically result in heightened foreign investments, fostering job creation, enhancing productivity, and driving economic progress.
- Global Commerce: Nations with superior credit ratings are perceived as more dependable and credible, making them preferred trading allies for other nations.
- Public Image: Nations with inferior credit ratings may be perceived as less dependable or steady, potentially undermining diplomatic ties and political sway.
- Critique of rating agencies
- Credibility: Well-known rating agencies openly disclose their methodology, relying on publicly accessible macroeconomic data from countries to bolster the trustworthiness of their assessments.
- Bias: These agencies faced significant backlash, accused of contributing to the onset of the U.S. financial crisis starting in 2007.
- Misleading metrics: They miscalculated the credit risk linked with structured credit products and were slow to adapt their ratings to worsening market conditions.
- Inaccurate: Allegations of methodological flaws and conflicts of interest were leveled against them repeatedly.
- Future Growth Prospects
- According to assessments by rating agencies, the nation is projected to experience a 7% annual growth rate if it continues on its current growth path and implements the outlined policy measures.
- This growth trajectory is anticipated to subsequently alleviate the government’s debt-to-GDP ratio.
- Over the past three years, real GDP growth has averaged 8.1% annually, the highest among nations in the Asia-Pacific region.
- The analysis also indicates the potential for the government to reduce its fiscal deficit, with the share expected to decrease from 7.9% of GDP in fiscal 2025 to 6.8% by fiscal 2028.
- The rating agency suggests that it may reconsider the country’s rating within the next 24 months if a prudent fiscal and monetary approach is adopted, focusing on reducing the government’s high debt and interest obligations while bolstering economic resilience.
- S&P stated, “Taking such cautious fiscal and monetary steps to address the government’s significant debt and interest burden while enhancing economic resilience could result in an improved rating over the next 24 months.”
About S&P Global Inc.
- S&P Global Inc. is a leading provider of financial information and analytics. The company delivers essential intelligence that powers decision-making in various sectors such as finance, business, and government. Its services include credit ratings, benchmarks, analytics, and data solutions, which are crucial for financial market participants to make informed decisions.
- Key Services and Divisions:
- S&P Global Ratings: One of the world’s largest credit rating agencies, providing credit ratings for sovereign, corporate, and municipal entities.
- S&P Global Market Intelligence: Offers data, analytics, and research covering a wide range of financial instruments and industries.
- S&P Dow Jones Indices: Manages some of the most well-known market indices, including the S&P 500.
- S&P Global Platts: Provides information and benchmarks for the energy and commodities markets.
- History and Background:
- Founded: 1860
- Headquarters: New York City, New York, USA
- Evolution: Initially known as The McGraw-Hill Companies, it rebranded to S&P Global Inc. in 2016 to reflect its core focus on financial information and analytics.
- Global Presence:
- S&P Global operates in multiple countries around the world, providing a broad range of financial information services to a diverse client base, including financial institutions, corporations, governments, and educational institutions.
- Global Presence:
- Market Influence:
- The company’s credit ratings and benchmarks are widely used by investors and other market participants to assess risk and performance, making S&P Global a critical player in the global financial ecosystem.
- Vision and Mission:
- S&P Global aims to provide essential intelligence that helps individuals and organizations make informed decisions with conviction, thus fostering growth and progress in global markets.
Disclaimer: The article may contain information pertaining to prior academic years; for further information, visit the exam’s “official or concerned website”.
Explore our courses: https://apnipathshala.com/courses/
Explore Our test Series: https://tests.apnipathshala.com/
- Why in the News?
- Inshort
- In a recent development S&P Global, the premier rating agency has changed India’s Sovereign rating outlook from stable to positive after a gap of 14 years.
- Major fiscal reforms and appropriate public spending stand as pillars of this development.
- However, the rating agency has retained the sovereign rating at the lowest investment grade ‘BBB-‘.
- In Depth
- In a statement issued on Wednesday, the US-based agency indicated that India’s rating might be upgraded within the next 24 months. This potential upgrade hinges on the country adopting prudent fiscal and monetary policies aimed at reducing the government’s substantial debt and interest expenses, while also bolstering its economic resilience. This rating update follows closely on the heels of the RBI’s release of a 2.10 lakh crore dividend to the government, intended to help bridge the fiscal deficit.
- S&P reported, “India’s outlook has been revised to positive due to strong growth and improved quality of government spending; BBB- long-term and ‘A-3’ short-term unsolicited foreign and local currency sovereign credit ratings are affirmed.”
- The agency highlighted that India’s vigorous economic growth is positively impacting its credit metrics. “We anticipate that sound economic fundamentals will support growth momentum over the next two to three years. Regardless of election outcomes, we expect a general continuity in economic reforms and fiscal policies,” S&P stated.
- “Our positive outlook on India is based on its strong economic growth, significant improvements in the quality of government spending, and a political commitment to fiscal consolidation. We believe these elements are coming together to enhance credit metrics,” S&P added.
- In Depth
- What are Sovereign Credit Ratings?
- A sovereign credit rating evaluates a country’s ability to fulfill its financial commitments, reflecting its creditworthiness.
- It gauges the credit risk linked to the nation’s bonds or other debt instruments.
- This rating is provided by agencies like Standard & Poor’s, Moody’s, and Fitch Ratings.
- India’s current ratings
- S&P and Fitch rate India ‘BBB-‘ and Moody’s ‘Baa3’, all indicative of the lowest-possible investment grade, but with a stable outlook.
- What does BBB mean?
- A ‘BBB’ rating indicates that expectations of default risk are currently low.
The capacity for payment of financial commitments is considered adequate, but adverse business or economic conditions are more likely to impair this capacity.

- What is a Rating Agency?
- Rating agencies evaluate the creditworthiness or potential of a country, equity, or debt. Investors use their reports to make informed decisions about investing in specific countries or companies within those regions.
- The agencies determine the financial stability and default risk of these entities. Essentially, these reports assist investors in determining the likelihood of receiving a return on their investment.
- What do they do?
- The agencies periodically re-evaluate previously assigned ratings after new developments geopolitical events or a significant economic announcement by the concerned entity.
- Their reports are sold and published in financial and daily newspapers.
- What grading system do they use?
- The three leading credit rating agencies, namely Standard & Poor’s, Moody’s, and Fitch, adhere to largely similar grading systems.
- Standard & Poor’s assigns its highest grade, AAA, to entities—be they countries, equities, or debts—with an extremely high ability to fulfill their financial obligations.
- Its grading scale includes letters A, B, and C, with the possibility of appending a single or double letter to indicate a higher grade.
- Moody’s categorizes ratings into short and long-term classifications. Its long-term ratings span from Aaa to C, with Aaa being the most favorable.
- Similarly, Fitch rates from AAA to D, with D representing the lowest rating. It employs the same sequence as Moody’s and Standard & Poor’s.
- The importance of such evaluations
- Access to Funding: Enhanced credit ratings enable nations to secure funding at reduced expenses, while lower ratings imply higher borrowing costs.
- Investment Analysis: Investors utilize credit ratings to gauge a nation’s creditworthiness and evaluate investment risks associated with it.
- Economic Advancement: Elevated credit ratings typically result in heightened foreign investments, fostering job creation, enhancing productivity, and driving economic progress.
- Global Commerce: Nations with superior credit ratings are perceived as more dependable and credible, making them preferred trading allies for other nations.
- Public Image: Nations with inferior credit ratings may be perceived as less dependable or steady, potentially undermining diplomatic ties and political sway.
- Critique of rating agencies
- Credibility: Well-known rating agencies openly disclose their methodology, relying on publicly accessible macroeconomic data from countries to bolster the trustworthiness of their assessments.
- Bias: These agencies faced significant backlash, accused of contributing to the onset of the U.S. financial crisis starting in 2007.
- Misleading metrics: They miscalculated the credit risk linked with structured credit products and were slow to adapt their ratings to worsening market conditions.
- Inaccurate: Allegations of methodological flaws and conflicts of interest were leveled against them repeatedly.
- Future Growth Prospects
- According to assessments by rating agencies, the nation is projected to experience a 7% annual growth rate if it continues on its current growth path and implements the outlined policy measures.
- This growth trajectory is anticipated to subsequently alleviate the government’s debt-to-GDP ratio.
- Over the past three years, real GDP growth has averaged 8.1% annually, the highest among nations in the Asia-Pacific region.
- The analysis also indicates the potential for the government to reduce its fiscal deficit, with the share expected to decrease from 7.9% of GDP in fiscal 2025 to 6.8% by fiscal 2028.
- The rating agency suggests that it may reconsider the country’s rating within the next 24 months if a prudent fiscal and monetary approach is adopted, focusing on reducing the government’s high debt and interest obligations while bolstering economic resilience.
- S&P stated, “Taking such cautious fiscal and monetary steps to address the government’s significant debt and interest burden while enhancing economic resilience could result in an improved rating over the next 24 months.”
About S&P Global Inc.
- S&P Global Inc. is a leading provider of financial information and analytics. The company delivers essential intelligence that powers decision-making in various sectors such as finance, business, and government. Its services include credit ratings, benchmarks, analytics, and data solutions, which are crucial for financial market participants to make informed decisions.
- Key Services and Divisions:
- S&P Global Ratings: One of the world’s largest credit rating agencies, providing credit ratings for sovereign, corporate, and municipal entities.
- S&P Global Market Intelligence: Offers data, analytics, and research covering a wide range of financial instruments and industries.
- S&P Dow Jones Indices: Manages some of the most well-known market indices, including the S&P 500.
- S&P Global Platts: Provides information and benchmarks for the energy and commodities markets.
- History and Background:
- Founded: 1860
- Headquarters: New York City, New York, USA
- Evolution: Initially known as The McGraw-Hill Companies, it rebranded to S&P Global Inc. in 2016 to reflect its core focus on financial information and analytics.
- Global Presence:
- S&P Global operates in multiple countries around the world, providing a broad range of financial information services to a diverse client base, including financial institutions, corporations, governments, and educational institutions.
- Global Presence:
- Market Influence:
- The company’s credit ratings and benchmarks are widely used by investors and other market participants to assess risk and performance, making S&P Global a critical player in the global financial ecosystem.
- Vision and Mission:
- S&P Global aims to provide essential intelligence that helps individuals and organizations make informed decisions with conviction, thus fostering growth and progress in global markets.
Disclaimer: The article may contain information pertaining to prior academic years; for further information, visit the exam’s “official or concerned website”.
Explore our courses: https://apnipathshala.com/courses/
Explore Our test Series: https://tests.apnipathshala.com/
- Why in the News?
- Inshort
- In a recent development S&P Global, the premier rating agency has changed India’s Sovereign rating outlook from stable to positive after a gap of 14 years.
- Major fiscal reforms and appropriate public spending stand as pillars of this development.
- However, the rating agency has retained the sovereign rating at the lowest investment grade ‘BBB-‘.
- In Depth
- In a statement issued on Wednesday, the US-based agency indicated that India’s rating might be upgraded within the next 24 months. This potential upgrade hinges on the country adopting prudent fiscal and monetary policies aimed at reducing the government’s substantial debt and interest expenses, while also bolstering its economic resilience. This rating update follows closely on the heels of the RBI’s release of a 2.10 lakh crore dividend to the government, intended to help bridge the fiscal deficit.
- S&P reported, “India’s outlook has been revised to positive due to strong growth and improved quality of government spending; BBB- long-term and ‘A-3’ short-term unsolicited foreign and local currency sovereign credit ratings are affirmed.”
- The agency highlighted that India’s vigorous economic growth is positively impacting its credit metrics. “We anticipate that sound economic fundamentals will support growth momentum over the next two to three years. Regardless of election outcomes, we expect a general continuity in economic reforms and fiscal policies,” S&P stated.
- “Our positive outlook on India is based on its strong economic growth, significant improvements in the quality of government spending, and a political commitment to fiscal consolidation. We believe these elements are coming together to enhance credit metrics,” S&P added.
- In Depth
- What are Sovereign Credit Ratings?
- A sovereign credit rating evaluates a country’s ability to fulfill its financial commitments, reflecting its creditworthiness.
- It gauges the credit risk linked to the nation’s bonds or other debt instruments.
- This rating is provided by agencies like Standard & Poor’s, Moody’s, and Fitch Ratings.
- India’s current ratings
- S&P and Fitch rate India ‘BBB-‘ and Moody’s ‘Baa3’, all indicative of the lowest-possible investment grade, but with a stable outlook.
- What does BBB mean?
- A ‘BBB’ rating indicates that expectations of default risk are currently low.
The capacity for payment of financial commitments is considered adequate, but adverse business or economic conditions are more likely to impair this capacity.

- What is a Rating Agency?
- Rating agencies evaluate the creditworthiness or potential of a country, equity, or debt. Investors use their reports to make informed decisions about investing in specific countries or companies within those regions.
- The agencies determine the financial stability and default risk of these entities. Essentially, these reports assist investors in determining the likelihood of receiving a return on their investment.
- What do they do?
- The agencies periodically re-evaluate previously assigned ratings after new developments geopolitical events or a significant economic announcement by the concerned entity.
- Their reports are sold and published in financial and daily newspapers.
- What grading system do they use?
- The three leading credit rating agencies, namely Standard & Poor’s, Moody’s, and Fitch, adhere to largely similar grading systems.
- Standard & Poor’s assigns its highest grade, AAA, to entities—be they countries, equities, or debts—with an extremely high ability to fulfill their financial obligations.
- Its grading scale includes letters A, B, and C, with the possibility of appending a single or double letter to indicate a higher grade.
- Moody’s categorizes ratings into short and long-term classifications. Its long-term ratings span from Aaa to C, with Aaa being the most favorable.
- Similarly, Fitch rates from AAA to D, with D representing the lowest rating. It employs the same sequence as Moody’s and Standard & Poor’s.
- The importance of such evaluations
- Access to Funding: Enhanced credit ratings enable nations to secure funding at reduced expenses, while lower ratings imply higher borrowing costs.
- Investment Analysis: Investors utilize credit ratings to gauge a nation’s creditworthiness and evaluate investment risks associated with it.
- Economic Advancement: Elevated credit ratings typically result in heightened foreign investments, fostering job creation, enhancing productivity, and driving economic progress.
- Global Commerce: Nations with superior credit ratings are perceived as more dependable and credible, making them preferred trading allies for other nations.
- Public Image: Nations with inferior credit ratings may be perceived as less dependable or steady, potentially undermining diplomatic ties and political sway.
- Critique of rating agencies
- Credibility: Well-known rating agencies openly disclose their methodology, relying on publicly accessible macroeconomic data from countries to bolster the trustworthiness of their assessments.
- Bias: These agencies faced significant backlash, accused of contributing to the onset of the U.S. financial crisis starting in 2007.
- Misleading metrics: They miscalculated the credit risk linked with structured credit products and were slow to adapt their ratings to worsening market conditions.
- Inaccurate: Allegations of methodological flaws and conflicts of interest were leveled against them repeatedly.
- Future Growth Prospects
- According to assessments by rating agencies, the nation is projected to experience a 7% annual growth rate if it continues on its current growth path and implements the outlined policy measures.
- This growth trajectory is anticipated to subsequently alleviate the government’s debt-to-GDP ratio.
- Over the past three years, real GDP growth has averaged 8.1% annually, the highest among nations in the Asia-Pacific region.
- The analysis also indicates the potential for the government to reduce its fiscal deficit, with the share expected to decrease from 7.9% of GDP in fiscal 2025 to 6.8% by fiscal 2028.
- The rating agency suggests that it may reconsider the country’s rating within the next 24 months if a prudent fiscal and monetary approach is adopted, focusing on reducing the government’s high debt and interest obligations while bolstering economic resilience.
- S&P stated, “Taking such cautious fiscal and monetary steps to address the government’s significant debt and interest burden while enhancing economic resilience could result in an improved rating over the next 24 months.”
About S&P Global Inc.
- S&P Global Inc. is a leading provider of financial information and analytics. The company delivers essential intelligence that powers decision-making in various sectors such as finance, business, and government. Its services include credit ratings, benchmarks, analytics, and data solutions, which are crucial for financial market participants to make informed decisions.
- Key Services and Divisions:
- S&P Global Ratings: One of the world’s largest credit rating agencies, providing credit ratings for sovereign, corporate, and municipal entities.
- S&P Global Market Intelligence: Offers data, analytics, and research covering a wide range of financial instruments and industries.
- S&P Dow Jones Indices: Manages some of the most well-known market indices, including the S&P 500.
- S&P Global Platts: Provides information and benchmarks for the energy and commodities markets.
- History and Background:
- Founded: 1860
- Headquarters: New York City, New York, USA
- Evolution: Initially known as The McGraw-Hill Companies, it rebranded to S&P Global Inc. in 2016 to reflect its core focus on financial information and analytics.
- Global Presence:
- S&P Global operates in multiple countries around the world, providing a broad range of financial information services to a diverse client base, including financial institutions, corporations, governments, and educational institutions.
- Global Presence:
- Market Influence:
- The company’s credit ratings and benchmarks are widely used by investors and other market participants to assess risk and performance, making S&P Global a critical player in the global financial ecosystem.
- Vision and Mission:
- S&P Global aims to provide essential intelligence that helps individuals and organizations make informed decisions with conviction, thus fostering growth and progress in global markets.
Disclaimer: The article may contain information pertaining to prior academic years; for further information, visit the exam’s “official or concerned website”.
Explore our courses: https://apnipathshala.com/courses/
Explore Our test Series: https://tests.apnipathshala.com/
- Why in the News?
- What are Sovereign Credit Ratings?
- What is a Rating Agency?
- Critique of rating agencies
- Future Growth Prospects
- About S&P Global Inc.
- Why in the News?
- Inshort
- In a recent development S&P Global, the premier rating agency has changed India’s Sovereign rating outlook from stable to positive after a gap of 14 years.
- Major fiscal reforms and appropriate public spending stand as pillars of this development.
- However, the rating agency has retained the sovereign rating at the lowest investment grade ‘BBB-‘.
- In Depth
- In a statement issued on Wednesday, the US-based agency indicated that India’s rating might be upgraded within the next 24 months. This potential upgrade hinges on the country adopting prudent fiscal and monetary policies aimed at reducing the government’s substantial debt and interest expenses, while also bolstering its economic resilience. This rating update follows closely on the heels of the RBI’s release of a 2.10 lakh crore dividend to the government, intended to help bridge the fiscal deficit.
- S&P reported, “India’s outlook has been revised to positive due to strong growth and improved quality of government spending; BBB- long-term and ‘A-3’ short-term unsolicited foreign and local currency sovereign credit ratings are affirmed.”
- The agency highlighted that India’s vigorous economic growth is positively impacting its credit metrics. “We anticipate that sound economic fundamentals will support growth momentum over the next two to three years. Regardless of election outcomes, we expect a general continuity in economic reforms and fiscal policies,” S&P stated.
- “Our positive outlook on India is based on its strong economic growth, significant improvements in the quality of government spending, and a political commitment to fiscal consolidation. We believe these elements are coming together to enhance credit metrics,” S&P added.
- In Depth
- What are Sovereign Credit Ratings?
- A sovereign credit rating evaluates a country’s ability to fulfill its financial commitments, reflecting its creditworthiness.
- It gauges the credit risk linked to the nation’s bonds or other debt instruments.
- This rating is provided by agencies like Standard & Poor’s, Moody’s, and Fitch Ratings.
- India’s current ratings
- S&P and Fitch rate India ‘BBB-‘ and Moody’s ‘Baa3’, all indicative of the lowest-possible investment grade, but with a stable outlook.
- What does BBB mean?
- A ‘BBB’ rating indicates that expectations of default risk are currently low.
The capacity for payment of financial commitments is considered adequate, but adverse business or economic conditions are more likely to impair this capacity.

- What is a Rating Agency?
- Rating agencies evaluate the creditworthiness or potential of a country, equity, or debt. Investors use their reports to make informed decisions about investing in specific countries or companies within those regions.
- The agencies determine the financial stability and default risk of these entities. Essentially, these reports assist investors in determining the likelihood of receiving a return on their investment.
- What do they do?
- The agencies periodically re-evaluate previously assigned ratings after new developments geopolitical events or a significant economic announcement by the concerned entity.
- Their reports are sold and published in financial and daily newspapers.
- What grading system do they use?
- The three leading credit rating agencies, namely Standard & Poor’s, Moody’s, and Fitch, adhere to largely similar grading systems.
- Standard & Poor’s assigns its highest grade, AAA, to entities—be they countries, equities, or debts—with an extremely high ability to fulfill their financial obligations.
- Its grading scale includes letters A, B, and C, with the possibility of appending a single or double letter to indicate a higher grade.
- Moody’s categorizes ratings into short and long-term classifications. Its long-term ratings span from Aaa to C, with Aaa being the most favorable.
- Similarly, Fitch rates from AAA to D, with D representing the lowest rating. It employs the same sequence as Moody’s and Standard & Poor’s.
- The importance of such evaluations
- Access to Funding: Enhanced credit ratings enable nations to secure funding at reduced expenses, while lower ratings imply higher borrowing costs.
- Investment Analysis: Investors utilize credit ratings to gauge a nation’s creditworthiness and evaluate investment risks associated with it.
- Economic Advancement: Elevated credit ratings typically result in heightened foreign investments, fostering job creation, enhancing productivity, and driving economic progress.
- Global Commerce: Nations with superior credit ratings are perceived as more dependable and credible, making them preferred trading allies for other nations.
- Public Image: Nations with inferior credit ratings may be perceived as less dependable or steady, potentially undermining diplomatic ties and political sway.
- Critique of rating agencies
- Credibility: Well-known rating agencies openly disclose their methodology, relying on publicly accessible macroeconomic data from countries to bolster the trustworthiness of their assessments.
- Bias: These agencies faced significant backlash, accused of contributing to the onset of the U.S. financial crisis starting in 2007.
- Misleading metrics: They miscalculated the credit risk linked with structured credit products and were slow to adapt their ratings to worsening market conditions.
- Inaccurate: Allegations of methodological flaws and conflicts of interest were leveled against them repeatedly.
- Future Growth Prospects
- According to assessments by rating agencies, the nation is projected to experience a 7% annual growth rate if it continues on its current growth path and implements the outlined policy measures.
- This growth trajectory is anticipated to subsequently alleviate the government’s debt-to-GDP ratio.
- Over the past three years, real GDP growth has averaged 8.1% annually, the highest among nations in the Asia-Pacific region.
- The analysis also indicates the potential for the government to reduce its fiscal deficit, with the share expected to decrease from 7.9% of GDP in fiscal 2025 to 6.8% by fiscal 2028.
- The rating agency suggests that it may reconsider the country’s rating within the next 24 months if a prudent fiscal and monetary approach is adopted, focusing on reducing the government’s high debt and interest obligations while bolstering economic resilience.
- S&P stated, “Taking such cautious fiscal and monetary steps to address the government’s significant debt and interest burden while enhancing economic resilience could result in an improved rating over the next 24 months.”
About S&P Global Inc.
- S&P Global Inc. is a leading provider of financial information and analytics. The company delivers essential intelligence that powers decision-making in various sectors such as finance, business, and government. Its services include credit ratings, benchmarks, analytics, and data solutions, which are crucial for financial market participants to make informed decisions.
- Key Services and Divisions:
- S&P Global Ratings: One of the world’s largest credit rating agencies, providing credit ratings for sovereign, corporate, and municipal entities.
- S&P Global Market Intelligence: Offers data, analytics, and research covering a wide range of financial instruments and industries.
- S&P Dow Jones Indices: Manages some of the most well-known market indices, including the S&P 500.
- S&P Global Platts: Provides information and benchmarks for the energy and commodities markets.
- History and Background:
- Founded: 1860
- Headquarters: New York City, New York, USA
- Evolution: Initially known as The McGraw-Hill Companies, it rebranded to S&P Global Inc. in 2016 to reflect its core focus on financial information and analytics.
- Global Presence:
- S&P Global operates in multiple countries around the world, providing a broad range of financial information services to a diverse client base, including financial institutions, corporations, governments, and educational institutions.
- Global Presence:
- Market Influence:
- The company’s credit ratings and benchmarks are widely used by investors and other market participants to assess risk and performance, making S&P Global a critical player in the global financial ecosystem.
- Vision and Mission:
- S&P Global aims to provide essential intelligence that helps individuals and organizations make informed decisions with conviction, thus fostering growth and progress in global markets.
Disclaimer: The article may contain information pertaining to prior academic years; for further information, visit the exam’s “official or concerned website”.
Explore our courses: https://apnipathshala.com/courses/
Explore Our test Series: https://tests.apnipathshala.com/
- Table of Contents
- Why in the News?
- What are Sovereign Credit Ratings?
- What is a Rating Agency?
- Critique of rating agencies
- Future Growth Prospects
- About S&P Global Inc.
- Table of Contents
- Why in the News?
- Inshort
- In a recent development S&P Global, the premier rating agency has changed India’s Sovereign rating outlook from stable to positive after a gap of 14 years.
- Major fiscal reforms and appropriate public spending stand as pillars of this development.
- However, the rating agency has retained the sovereign rating at the lowest investment grade ‘BBB-‘.
- In Depth
- In a statement issued on Wednesday, the US-based agency indicated that India’s rating might be upgraded within the next 24 months. This potential upgrade hinges on the country adopting prudent fiscal and monetary policies aimed at reducing the government’s substantial debt and interest expenses, while also bolstering its economic resilience. This rating update follows closely on the heels of the RBI’s release of a 2.10 lakh crore dividend to the government, intended to help bridge the fiscal deficit.
- S&P reported, “India’s outlook has been revised to positive due to strong growth and improved quality of government spending; BBB- long-term and ‘A-3’ short-term unsolicited foreign and local currency sovereign credit ratings are affirmed.”
- The agency highlighted that India’s vigorous economic growth is positively impacting its credit metrics. “We anticipate that sound economic fundamentals will support growth momentum over the next two to three years. Regardless of election outcomes, we expect a general continuity in economic reforms and fiscal policies,” S&P stated.
- “Our positive outlook on India is based on its strong economic growth, significant improvements in the quality of government spending, and a political commitment to fiscal consolidation. We believe these elements are coming together to enhance credit metrics,” S&P added.
- In Depth
- What are Sovereign Credit Ratings?
- A sovereign credit rating evaluates a country’s ability to fulfill its financial commitments, reflecting its creditworthiness.
- It gauges the credit risk linked to the nation’s bonds or other debt instruments.
- This rating is provided by agencies like Standard & Poor’s, Moody’s, and Fitch Ratings.
- India’s current ratings
- S&P and Fitch rate India ‘BBB-‘ and Moody’s ‘Baa3’, all indicative of the lowest-possible investment grade, but with a stable outlook.
- What does BBB mean?
- A ‘BBB’ rating indicates that expectations of default risk are currently low.
The capacity for payment of financial commitments is considered adequate, but adverse business or economic conditions are more likely to impair this capacity.

- What is a Rating Agency?
- Rating agencies evaluate the creditworthiness or potential of a country, equity, or debt. Investors use their reports to make informed decisions about investing in specific countries or companies within those regions.
- The agencies determine the financial stability and default risk of these entities. Essentially, these reports assist investors in determining the likelihood of receiving a return on their investment.
- What do they do?
- The agencies periodically re-evaluate previously assigned ratings after new developments geopolitical events or a significant economic announcement by the concerned entity.
- Their reports are sold and published in financial and daily newspapers.
- What grading system do they use?
- The three leading credit rating agencies, namely Standard & Poor’s, Moody’s, and Fitch, adhere to largely similar grading systems.
- Standard & Poor’s assigns its highest grade, AAA, to entities—be they countries, equities, or debts—with an extremely high ability to fulfill their financial obligations.
- Its grading scale includes letters A, B, and C, with the possibility of appending a single or double letter to indicate a higher grade.
- Moody’s categorizes ratings into short and long-term classifications. Its long-term ratings span from Aaa to C, with Aaa being the most favorable.
- Similarly, Fitch rates from AAA to D, with D representing the lowest rating. It employs the same sequence as Moody’s and Standard & Poor’s.
- The importance of such evaluations
- Access to Funding: Enhanced credit ratings enable nations to secure funding at reduced expenses, while lower ratings imply higher borrowing costs.
- Investment Analysis: Investors utilize credit ratings to gauge a nation’s creditworthiness and evaluate investment risks associated with it.
- Economic Advancement: Elevated credit ratings typically result in heightened foreign investments, fostering job creation, enhancing productivity, and driving economic progress.
- Global Commerce: Nations with superior credit ratings are perceived as more dependable and credible, making them preferred trading allies for other nations.
- Public Image: Nations with inferior credit ratings may be perceived as less dependable or steady, potentially undermining diplomatic ties and political sway.
- Critique of rating agencies
- Credibility: Well-known rating agencies openly disclose their methodology, relying on publicly accessible macroeconomic data from countries to bolster the trustworthiness of their assessments.
- Bias: These agencies faced significant backlash, accused of contributing to the onset of the U.S. financial crisis starting in 2007.
- Misleading metrics: They miscalculated the credit risk linked with structured credit products and were slow to adapt their ratings to worsening market conditions.
- Inaccurate: Allegations of methodological flaws and conflicts of interest were leveled against them repeatedly.
- Future Growth Prospects
- According to assessments by rating agencies, the nation is projected to experience a 7% annual growth rate if it continues on its current growth path and implements the outlined policy measures.
- This growth trajectory is anticipated to subsequently alleviate the government’s debt-to-GDP ratio.
- Over the past three years, real GDP growth has averaged 8.1% annually, the highest among nations in the Asia-Pacific region.
- The analysis also indicates the potential for the government to reduce its fiscal deficit, with the share expected to decrease from 7.9% of GDP in fiscal 2025 to 6.8% by fiscal 2028.
- The rating agency suggests that it may reconsider the country’s rating within the next 24 months if a prudent fiscal and monetary approach is adopted, focusing on reducing the government’s high debt and interest obligations while bolstering economic resilience.
- S&P stated, “Taking such cautious fiscal and monetary steps to address the government’s significant debt and interest burden while enhancing economic resilience could result in an improved rating over the next 24 months.”
About S&P Global Inc.
- S&P Global Inc. is a leading provider of financial information and analytics. The company delivers essential intelligence that powers decision-making in various sectors such as finance, business, and government. Its services include credit ratings, benchmarks, analytics, and data solutions, which are crucial for financial market participants to make informed decisions.
- Key Services and Divisions:
- S&P Global Ratings: One of the world’s largest credit rating agencies, providing credit ratings for sovereign, corporate, and municipal entities.
- S&P Global Market Intelligence: Offers data, analytics, and research covering a wide range of financial instruments and industries.
- S&P Dow Jones Indices: Manages some of the most well-known market indices, including the S&P 500.
- S&P Global Platts: Provides information and benchmarks for the energy and commodities markets.
- History and Background:
- Founded: 1860
- Headquarters: New York City, New York, USA
- Evolution: Initially known as The McGraw-Hill Companies, it rebranded to S&P Global Inc. in 2016 to reflect its core focus on financial information and analytics.
- Global Presence:
- S&P Global operates in multiple countries around the world, providing a broad range of financial information services to a diverse client base, including financial institutions, corporations, governments, and educational institutions.
- Global Presence:
- Market Influence:
- The company’s credit ratings and benchmarks are widely used by investors and other market participants to assess risk and performance, making S&P Global a critical player in the global financial ecosystem.
- Vision and Mission:
- S&P Global aims to provide essential intelligence that helps individuals and organizations make informed decisions with conviction, thus fostering growth and progress in global markets.
Disclaimer: The article may contain information pertaining to prior academic years; for further information, visit the exam’s “official or concerned website”.
Explore our courses: https://apnipathshala.com/courses/
Explore Our test Series: https://tests.apnipathshala.com/
- Table of Contents
- Why in the News?
- What are Sovereign Credit Ratings?
- What is a Rating Agency?
- Critique of rating agencies
- Future Growth Prospects
- About S&P Global Inc.
- Table of Contents
- Why in the News?
- Inshort
- In a recent development S&P Global, the premier rating agency has changed India’s Sovereign rating outlook from stable to positive after a gap of 14 years.
- Major fiscal reforms and appropriate public spending stand as pillars of this development.
- However, the rating agency has retained the sovereign rating at the lowest investment grade ‘BBB-‘.
- In Depth
- In a statement issued on Wednesday, the US-based agency indicated that India’s rating might be upgraded within the next 24 months. This potential upgrade hinges on the country adopting prudent fiscal and monetary policies aimed at reducing the government’s substantial debt and interest expenses, while also bolstering its economic resilience. This rating update follows closely on the heels of the RBI’s release of a 2.10 lakh crore dividend to the government, intended to help bridge the fiscal deficit.
- S&P reported, “India’s outlook has been revised to positive due to strong growth and improved quality of government spending; BBB- long-term and ‘A-3’ short-term unsolicited foreign and local currency sovereign credit ratings are affirmed.”
- The agency highlighted that India’s vigorous economic growth is positively impacting its credit metrics. “We anticipate that sound economic fundamentals will support growth momentum over the next two to three years. Regardless of election outcomes, we expect a general continuity in economic reforms and fiscal policies,” S&P stated.
- “Our positive outlook on India is based on its strong economic growth, significant improvements in the quality of government spending, and a political commitment to fiscal consolidation. We believe these elements are coming together to enhance credit metrics,” S&P added.
- In Depth
- What are Sovereign Credit Ratings?
- A sovereign credit rating evaluates a country’s ability to fulfill its financial commitments, reflecting its creditworthiness.
- It gauges the credit risk linked to the nation’s bonds or other debt instruments.
- This rating is provided by agencies like Standard & Poor’s, Moody’s, and Fitch Ratings.
- India’s current ratings
- S&P and Fitch rate India ‘BBB-‘ and Moody’s ‘Baa3’, all indicative of the lowest-possible investment grade, but with a stable outlook.
- What does BBB mean?
- A ‘BBB’ rating indicates that expectations of default risk are currently low.
The capacity for payment of financial commitments is considered adequate, but adverse business or economic conditions are more likely to impair this capacity.

- What is a Rating Agency?
- Rating agencies evaluate the creditworthiness or potential of a country, equity, or debt. Investors use their reports to make informed decisions about investing in specific countries or companies within those regions.
- The agencies determine the financial stability and default risk of these entities. Essentially, these reports assist investors in determining the likelihood of receiving a return on their investment.
- What do they do?
- The agencies periodically re-evaluate previously assigned ratings after new developments geopolitical events or a significant economic announcement by the concerned entity.
- Their reports are sold and published in financial and daily newspapers.
- What grading system do they use?
- The three leading credit rating agencies, namely Standard & Poor’s, Moody’s, and Fitch, adhere to largely similar grading systems.
- Standard & Poor’s assigns its highest grade, AAA, to entities—be they countries, equities, or debts—with an extremely high ability to fulfill their financial obligations.
- Its grading scale includes letters A, B, and C, with the possibility of appending a single or double letter to indicate a higher grade.
- Moody’s categorizes ratings into short and long-term classifications. Its long-term ratings span from Aaa to C, with Aaa being the most favorable.
- Similarly, Fitch rates from AAA to D, with D representing the lowest rating. It employs the same sequence as Moody’s and Standard & Poor’s.
- The importance of such evaluations
- Access to Funding: Enhanced credit ratings enable nations to secure funding at reduced expenses, while lower ratings imply higher borrowing costs.
- Investment Analysis: Investors utilize credit ratings to gauge a nation’s creditworthiness and evaluate investment risks associated with it.
- Economic Advancement: Elevated credit ratings typically result in heightened foreign investments, fostering job creation, enhancing productivity, and driving economic progress.
- Global Commerce: Nations with superior credit ratings are perceived as more dependable and credible, making them preferred trading allies for other nations.
- Public Image: Nations with inferior credit ratings may be perceived as less dependable or steady, potentially undermining diplomatic ties and political sway.
- Critique of rating agencies
- Credibility: Well-known rating agencies openly disclose their methodology, relying on publicly accessible macroeconomic data from countries to bolster the trustworthiness of their assessments.
- Bias: These agencies faced significant backlash, accused of contributing to the onset of the U.S. financial crisis starting in 2007.
- Misleading metrics: They miscalculated the credit risk linked with structured credit products and were slow to adapt their ratings to worsening market conditions.
- Inaccurate: Allegations of methodological flaws and conflicts of interest were leveled against them repeatedly.
- Future Growth Prospects
- According to assessments by rating agencies, the nation is projected to experience a 7% annual growth rate if it continues on its current growth path and implements the outlined policy measures.
- This growth trajectory is anticipated to subsequently alleviate the government’s debt-to-GDP ratio.
- Over the past three years, real GDP growth has averaged 8.1% annually, the highest among nations in the Asia-Pacific region.
- The analysis also indicates the potential for the government to reduce its fiscal deficit, with the share expected to decrease from 7.9% of GDP in fiscal 2025 to 6.8% by fiscal 2028.
- The rating agency suggests that it may reconsider the country’s rating within the next 24 months if a prudent fiscal and monetary approach is adopted, focusing on reducing the government’s high debt and interest obligations while bolstering economic resilience.
- S&P stated, “Taking such cautious fiscal and monetary steps to address the government’s significant debt and interest burden while enhancing economic resilience could result in an improved rating over the next 24 months.”
About S&P Global Inc.
- S&P Global Inc. is a leading provider of financial information and analytics. The company delivers essential intelligence that powers decision-making in various sectors such as finance, business, and government. Its services include credit ratings, benchmarks, analytics, and data solutions, which are crucial for financial market participants to make informed decisions.
- Key Services and Divisions:
- S&P Global Ratings: One of the world’s largest credit rating agencies, providing credit ratings for sovereign, corporate, and municipal entities.
- S&P Global Market Intelligence: Offers data, analytics, and research covering a wide range of financial instruments and industries.
- S&P Dow Jones Indices: Manages some of the most well-known market indices, including the S&P 500.
- S&P Global Platts: Provides information and benchmarks for the energy and commodities markets.
- History and Background:
- Founded: 1860
- Headquarters: New York City, New York, USA
- Evolution: Initially known as The McGraw-Hill Companies, it rebranded to S&P Global Inc. in 2016 to reflect its core focus on financial information and analytics.
- Global Presence:
- S&P Global operates in multiple countries around the world, providing a broad range of financial information services to a diverse client base, including financial institutions, corporations, governments, and educational institutions.
- Global Presence:
- Market Influence:
- The company’s credit ratings and benchmarks are widely used by investors and other market participants to assess risk and performance, making S&P Global a critical player in the global financial ecosystem.
- Vision and Mission:
- S&P Global aims to provide essential intelligence that helps individuals and organizations make informed decisions with conviction, thus fostering growth and progress in global markets.
Disclaimer: The article may contain information pertaining to prior academic years; for further information, visit the exam’s “official or concerned website”.
Explore our courses: https://apnipathshala.com/courses/
Explore Our test Series: https://tests.apnipathshala.com/










